Getting Started with Geodatabase in ArcGIS: A Beginner’s Guide
In this Tutorial Learn, how to create a Geodatabase in ArcGIS.
What is a Geodatabase?
A Geodatabase (GDB) is a Database designed to store, query, and manipulate geographic information and spatial data. It’s like a digital container that holds all the different types of map-related information you need—such as locations, images, tables, and rules about how data behaves.
The GDB is designed to make full use of the capabilities of ArcGIS Desktop and ArcGIS Server. ArcGIS Geodatabase is a collection of geographic datasets of various types, such as IBM Db2, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, or SAP HANA.
In a geodatabase, we can store:
- Geometry – the shape and location of features on a map (like points, lines, or areas)
- Attributes – details about each feature (like names, values, or categories)
- Spatial reference system – information about the map’s scale and position on the earth
- Behavioral rules – rules that control how data behaves and relates to other data
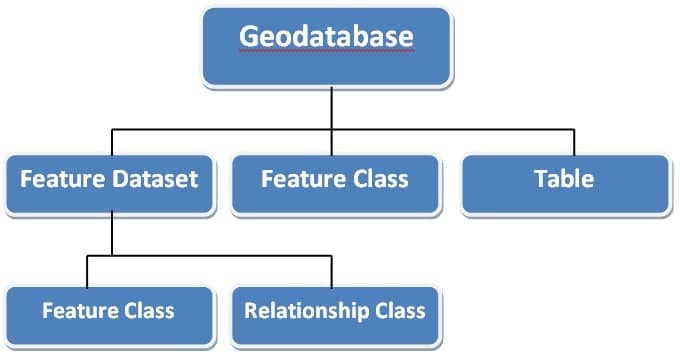
Various types of geographic datasets can be collected within a geodatabase, including;
- Feature classes (points, lines, polygons)
- Attribute tables
- Raster datasets (like satellite images)
- Network datasets, (used for roads, utilities, etc.)
- Topologies, (to manage spatial relationships)
- And more…
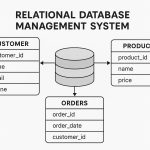
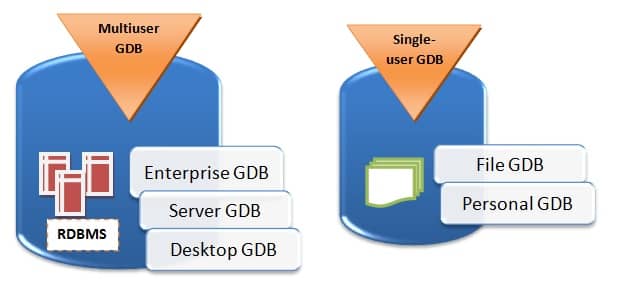
Geodatabases can be stored in Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) or in a system of files, such as a file geo-database.
We can use a geodatabase in two main ways:
- As a simple folder (single) stored on your computer (called a file geodatabase), or
- As part of a larger multi-user system used in organizations (called an enterprise
geodatabase)
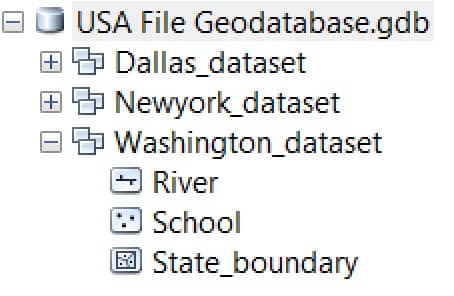
Geodatabase Structure
Geodatabase Data Model
The various geographic datasets and tables in an instance of a geo-database.
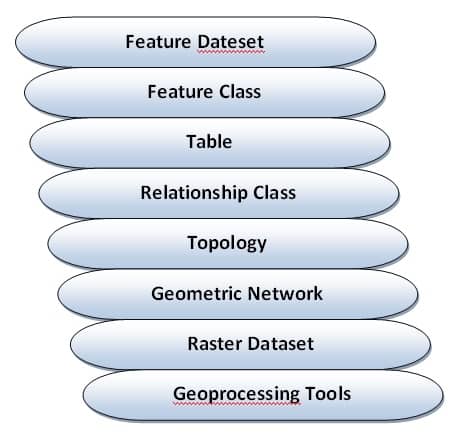
Types of Data in a Geodatabase:
The geodatabase supports all the different types of GIS data that can be used by ArcGIS, such as attribute data, geographic features, satellite and aerial images, CAD data, surface modeling or 3D data, GPS coordinates, and survey measurements.
The core of a geodatabase is made up of three main types of data:
- Feature Classes – These are collections of geographic features like points (e.g., wells),
lines (e.g., roads), or polygons (e.g., land parcels). - Raster Datasets – These are image-like data such as aerial photos or satellite images.
- Tables – These hold non-spatial information, such as names, numbers, or categories
related to the features.
How Data Is Stored:
All data in a geodatabase is stored in tables. Each feature—like a road or a building—is stored as a row in a table. One of the fields in that row holds the shape of the feature (such as the coordinates for a polygon). For example, in a polygon feature class, each row represents one area, and the Shape field stores the geometry that defines its shape.
Types of geodatabases:
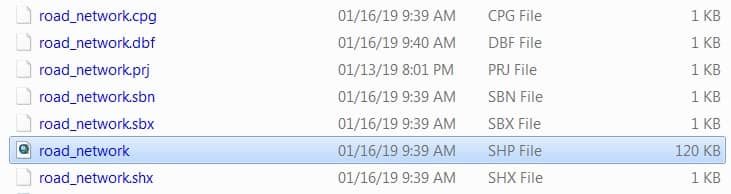
There are different types of geodatabases, but one of the most commonly used in GIS is the File Geodatabase.
A File Geodatabase is stored as a collection of files inside a folder with a .gdb extension. Each dataset (like a map layer or table) is saved as a separate file within that folder. Each file can be as large as 1 terabyte (TB). However, if needed, this limit can be increased up to 4 TB or even 256 TB.
Managing a File Geodatabase:
When using a file geodatabase, there are a few tasks we can do to help keep it running smoothly.
Some tasks are important for maintaining good performance, like:
- Compacting the geodatabase – This helps reduce its size and improve speed.
- Re-creating the spatial index – This keeps spatial searches and queries working efficiently.
Whereas, other tasks are optional, such as:
- Compressing vector data – To save space and make the data read-only.
- Creating a licensed file geodatabase – To protect your data and control who can use it.
These management steps help ensure geodatabase stays fast, organized, and secure.
Create a New File Geodatabase in ArcGIS
A File Geodatabase can be used simultaneously by several users, but only one user at a time can edit the same data.
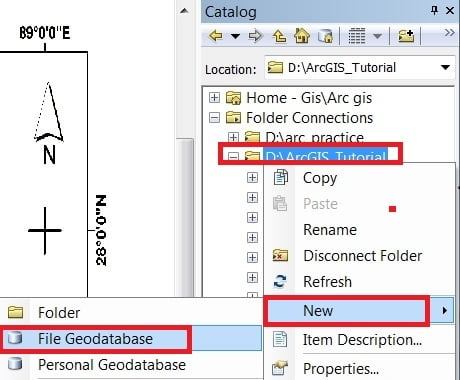
In the Catalog window expand your folder (ex.- ArcGIS_Tutorial), Right click > New, select File Geodatabase.
Create Feature Dataset within File Geodatabase
A Feature Dataset is a collection of related feature classes that share a common Coordinate system.
Feature datasets are used to spatially integrate related feature classes. Their primary purpose is to organize related feature classes into a common dataset for better management purposes. Here are the steps to create a feature dataset:
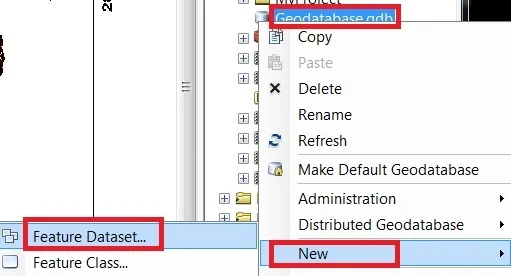
1. Right-click already create File Geodatabase (.gdb), now select Feature Dataset.
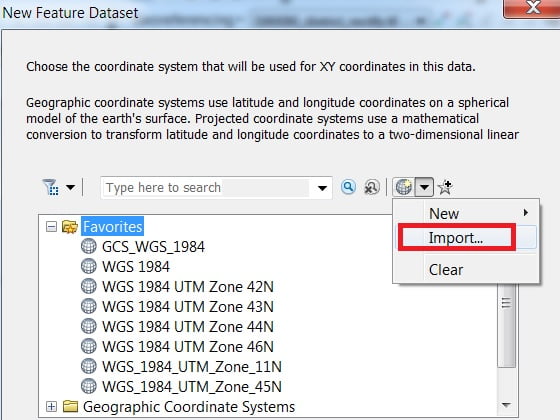
2. Write Name (sikkim_project) and click the Next button. Click Add Coordinate System Tool > Import option and select your rectified map.
3. Click Next button all are Default option is OK just Skip it and Click Finish button to close the wizard.
Create Feature Classes within Feature Dataset
A Feature Class is a collection of geographic features that share the same geometry type (such as point. line, or polygon). And the same attribute fields for a common area.
Select the Map Feature dataset (sikkim_project), click the right button of the mouse > New > Feature Class.
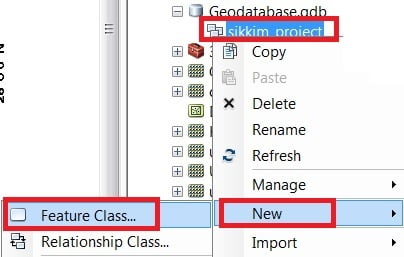
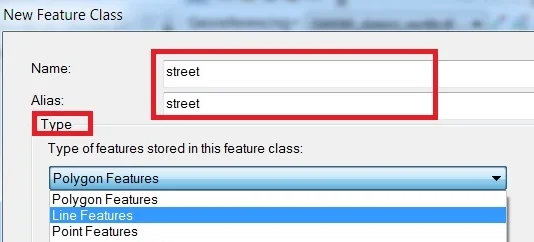
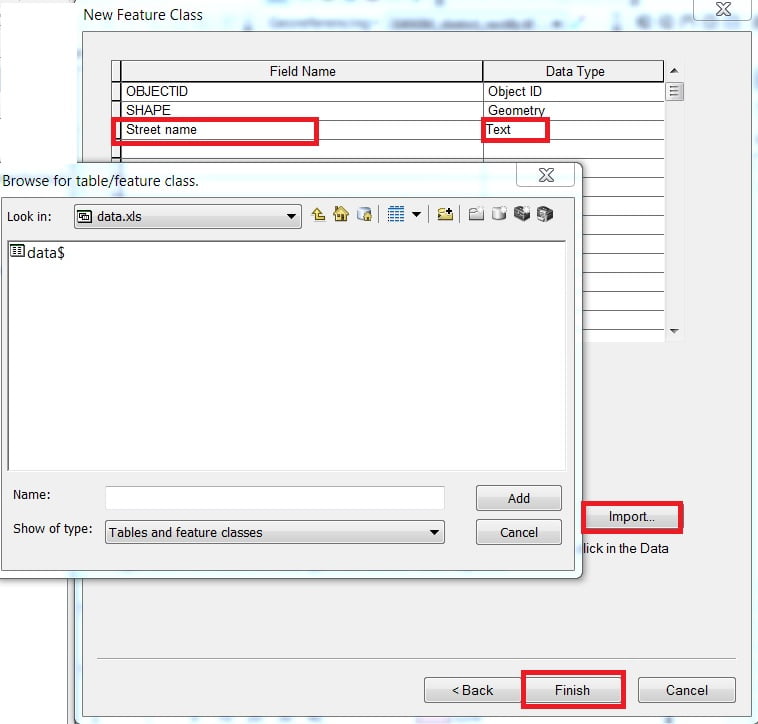
Type Name and Alias, select Feature Type. The database storage configuration wizard, do not make any changes, just click the Next button. In the fields creation wizard, add new Field and select type in the field blank row. You can also import data to click the Import button. Click the Finish button.
Create Table in File Geodatabase
The attributes and properties of Geographic objects are stored and managed in Tables. Tabular information is the basis of geographic features, allowing you to visualize, query, and analyze your data. You create here one such type of Table for storing both spatial and attribute information.
1. In the Catalog window, select the Geodatabase (.gdb), Right click > New > Table.
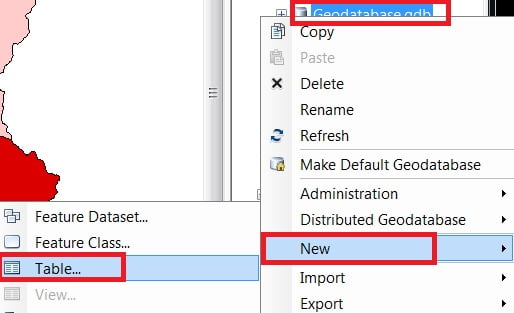
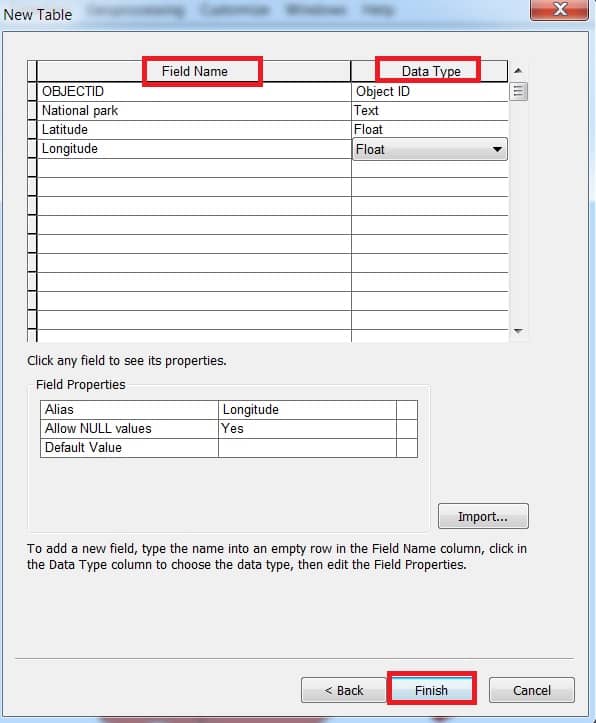
2. Write Name and Alias (sikkimNationalpark) on the table. Click the Next button. In the database storage configuration wizard, do not make any changes, just click the Next button.
In the fields creation wizard, click the blank row in the Field Name, write a name, and then select the data type. Finally, click the Finish button.
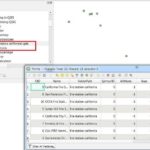
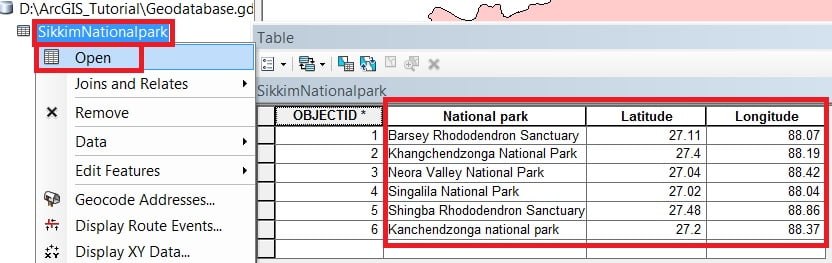
3. Click the Editor Button present on the Editor Toolbar and select Start Editing. Select the table (sikkimNationalpark) from TOC (Table Of Contents) Window. Right-click and choose Open, Add the records within this table.
Save edits and Stop editing session.
Adding ‘X’ and ‘Y’ coordinate data as a layer to the map
4. Select Table (SikkimNationalpark) from the TOC window, Right-click, and choose Display XY Data.
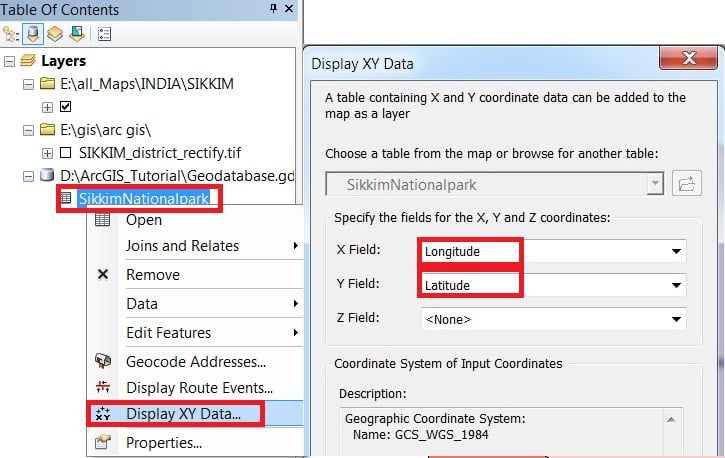
5. In Display, ‘XY’ Data window, X and Y field automatically default selected, ‘X‘ field is Longitude, and ‘Y‘ field is Latitude. The coordinates system is automatically selected. Finally, click the OK button to close the Add XY Data window.
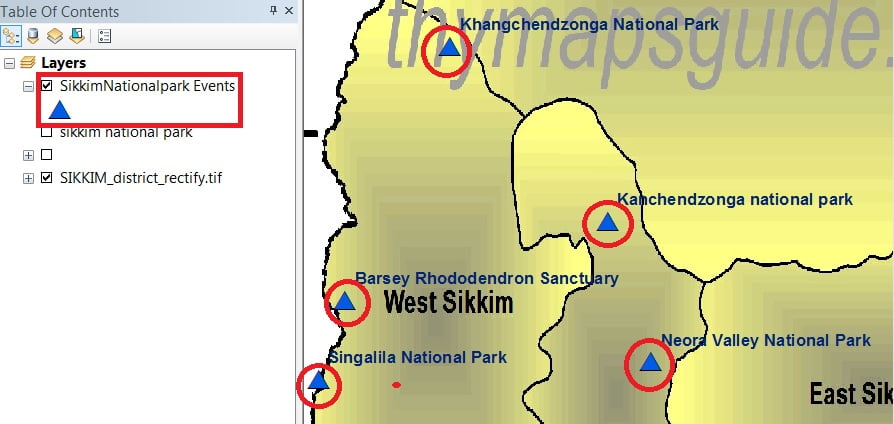
Now Display your Data in the Map Frame.
Geodatabase vs Shapefile
Compare between Shapefile and Geodatabase:
| Category | Geodatabase | Shapefile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A geodatabase is a collection of spatial and non-spatial data stored in a relational database management system (RDBMS. | A shapefile is a simple file-based format that stores geometry and attributes of a single feature class. |
| File Format | .gdb | .shp |
| File size limit | Depend on your computer hard-drive storage space | 2 GB |
| Field name length limit | 64 characters | 10 characters |
| Data types | Vector | Vector, and Raster |
| Topology | Supported | Not supported |
| NULL values | Supported | Can’t store NULL, use 0 instead |
| Geometries Comparesion | Point Multipoints Polyline Polygon Polyline with Measure Feature Class Feature Dataset | Point Multipoints Polyline Polygon Polyline with Measure .shp, .shx, .dbf Feature Dataset |