Table of Contents
Vector Data & Raster Data
Vector Data
A Vector data feature its represent shape using Geometry. The geometry is made up of one or more interconnected vertices. A vertex describes a position in space using an X, Y and optionally Z axis. Geometries which have vertices with a Z axis are often referred to as 3D since they describe height or depth at each vertex, but not both.
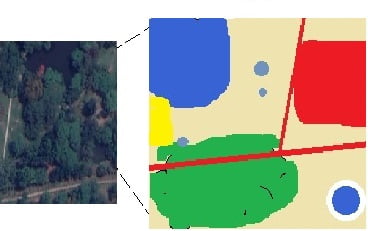
Vector Database is simply XY coordinates. Generally, they are a Latitude and Longitude value. The Vector data represents are points, lines, and polygons.
Raster Data
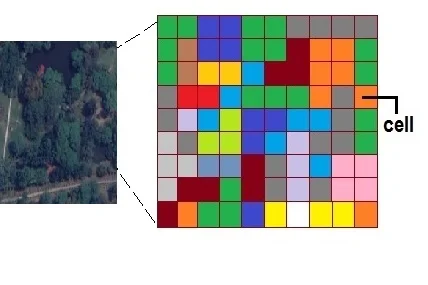
Raster data represent real world data, within the GIS environment. Its consists of a matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid) where each cell contains a value representing information. Raster database represents continuous data such as Elevation, Slope, Surface.
Raster Database are Digital Aerial Photographs, Satellites imagery, Digital pictures, or even scanned Maps.
Vector Data vs Raster Data
Raster Data
- Grid and cells
- For continuous data such as elevation, slope, surfaces
Vector Data
- A series of x,y coordinates
- For discrete data represented as points, lines, polygons
Difference Between Raster Data vs Vector Data
Raster Data
Vector Data
Advantages
- Easy and efficient overlaying
- Compatible with remote sensing imagery
- Efficient to represents continuous data
- Simple data structure
- Smaller file size
- Editing is very Easy
- Proper identity for discrete objects, like point, line or polygon
- Efficient Topological relationship
- Accurate projection transformation
Disadvantages
- Difficult overlay operations
- Not Compatible with remote sensing imagery
- That is Not proper represents continuous data
- Complex data structure
- Larger file size
- Difficult to edit
- It’s a pixel series, so not accurate identity the objects
- Did not build Topological relationship
- Inefficient projection transformation
Raster & Vector File Format
Raster File Formats
| File Formats | Full Form |
|---|---|
| BMP | Bit Map Image |
| ECW | Enhanced Compression Wavelet |
| JPEG(JPG) | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| PCX | Personal Computer Exchange |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| TIFF | Tagged Image File Format |
| GIF | Graphics Interchange Format |
| PICT | Image Originator Apple Computer |
| RLC | Run Length Compressed |
| IGS | Image in Grayscale |
| GEOSPOT | Spot Image Corp.(Georeferenced Image) |
| GEOTIFF | Georeferenced Tiff Image |
| MRSID | Multiresolution Seamless Image Database |
| Exif | Exchangeable Image File Format |
| PSD | Adobe PhotoShop Document |
| ADRG | Arc Digitized Raster Graphics |
| SDTS | Spatial Data Transfer Standard |
| IMG | Erdas Imagine Image |
| CALS | Computer-aided Acquisition Logistics and support |
| TGA(TARGA) | A Simple run length encoded image format |
Vector File Formats
| File Formats | Full Form |
|---|---|
| E00 | Arc Export |
| COVERAGE | Arc/INFO Coverage |
| CGM | Computer Graphics Metafile |
| DWG | AutoCAD Drawing file |
| DXF | Data Interchange File |
| HPGL | Hewlett Packard Graphic Language |
| GDB | Geodatabase |
| MDB | Personal Geodatabase |
| MIF/MID | Mapinfo Data Transfer Files |
| SVG | Scalable Vector Graphics |
| ODG | OpenDocument Graphics |
| DGN | MicroStation Design File |
| SDTS | Spatial Data Transfer System |
| TIGER | Topological Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing |
| SHP | Shapefile |
| VPF | Vector Product Format |
| VML | Vector Markup Language |
| CDR | CorelDRAW |
| HVIF | Haiku Vector Icon Format |
| AMF | Additive Manufacturing File Format |
