GIS Layers
Geographic Information System (GIS) as one of desciplines for spatial data science. In this lesson discuss about GIS Layering.
GIS Data Layers
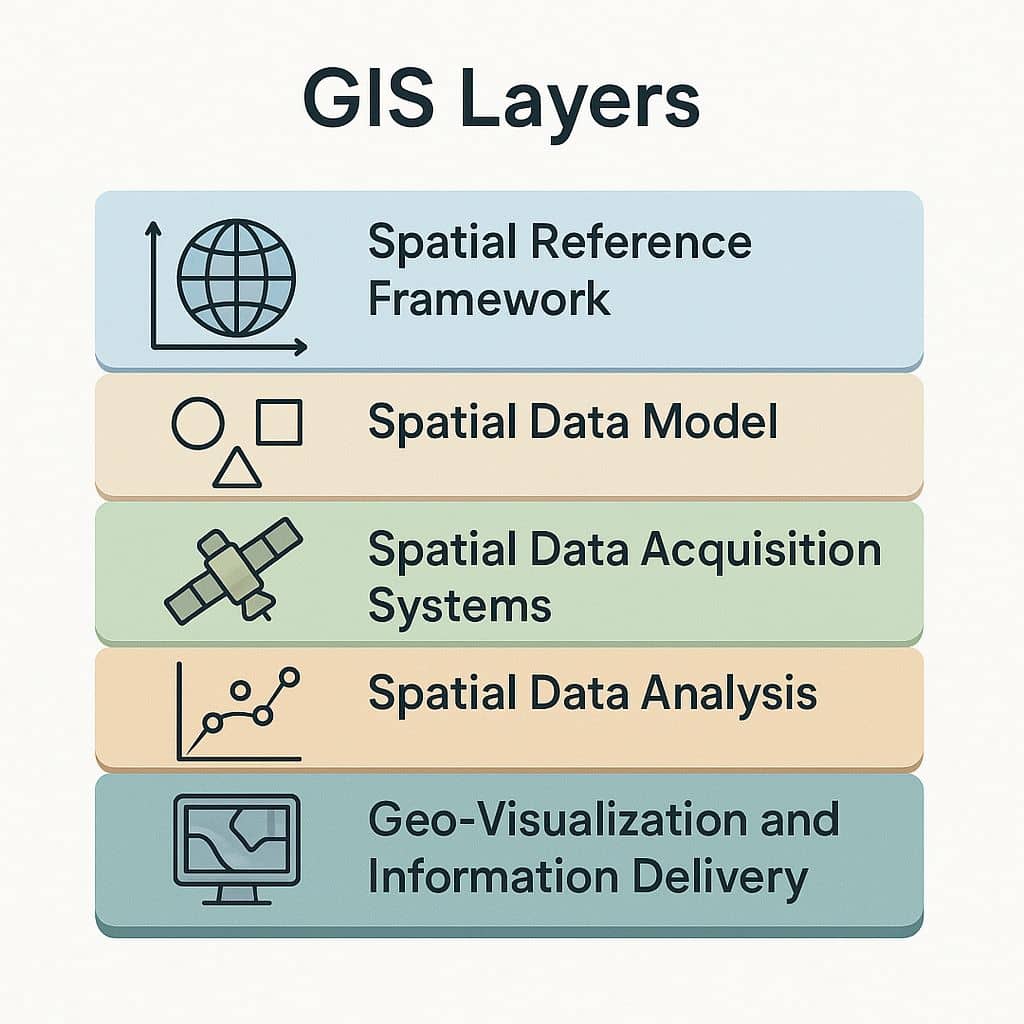
Five Layers of GIS, for Spatial Data Science and application.
- Spatial reference framework
- Spatial data model
- Spatial data acquisition systems
- Spatial data analysis
- Geo-visualization and information delivery
1. Spatial reference framework
Spatial Reference Framework is known as A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS). It’s included physical Earth, Geoid, Ellipsoid, Datum, and Map projection.
Examples: WGS 84, UTM zones, geographic vs. projected coordinate systems.
2. Spatial data model
Spatial Data Models represent the spatial reality in two spatial data models, i)Vector data model and ii) Raster data model. Vector data represents spatial and attribute components and relationship. Others spatial data models, like Network model, TIN model, DEM model, etc.
Examples: Roads (lines), Land parcels (polygons), Temperature (raster)
3. Spatial data acquisition systems
Spatial Data Acquisition Systems will cover how to acquire and produce spatial data. Example of Spatial Data Acquisition Systems, Conventional survey, GPS, GNSS, Photogrammetry/ Satellite image, Lidar, etc.
4. Spatial data analysis
Spatial Data Analysis is, how to extract useful and valuable information from spatial data. The Spatial analysis more advanced algorithms to find out data structure. Example of Spatial Data Analysis, Proximity analysis, Spatial Interpolation, Network analysis, Terrain analysis, Factor analysis, etc.
5. Geo-visualization and information delivery
Geo-visualization and Information Delivery is a powerful aspect, and negative potentials of cartographic representations of the spatial phenomenon. Geo-visualization uses for Topography creation, Scale and Map generation, Map animation, Web mapping service, etc.