GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
GNSS stand for Global Navigation Satellite System. It is a general term describing any Satellite constellation that provides positioning, navigation, and timing services on a global or regional basis.

Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) which is basically a constellation of constellations of systems like NAVSTAR GPS and GLONASS, wherein the services of more than one constellation is used to derive the position, velocity and timing.
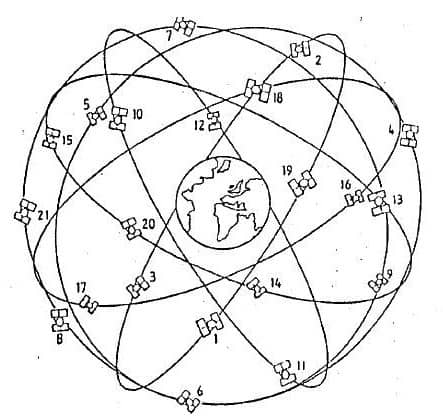
- NAVSTAR GPS: The NAVSTAR GPS (Navigation System Time and Ranging Global Positioning System) is a satellite based radio navigation system providing precise three-dimensional position, course and time information to suitably equipped user.
| Development | 1973 |
| Manufacturer | Rockwell International |
| Altitude | 10,900 nautical miles or 20, 2000 km. |
| Weight | 1900 1bs. (in Orbit) |
| Size | 17 ft with solar panels extended |
| Orbital Period | 12 hours |
| Orbital Plane | 55 degrees to equatorial plane |
| Planned Life span | 7.5 years |
| Current constellation | 24 Block IIRS production satellites |
| Future satellites | 21 Block IIRS developed by Martin Marietta |
- GLONASS: Global Navigation & Surveying System (GLONASS) a similar system to NAVSTAR GPS was developed by Russia (former Soviet Union) and is now a valuable complementary system to GPS and a part of GNSS wherein both NAVSTAR GPS & GLONASS signals are utilized together.
Table of Contents
GNSS Satellite System
GPS
The GPS (Global Positioning System) is a worldwide satellite-based radio navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. It’s used to determine accurate geodetic position on the earth surface.
In 1973 the U.S. Department of Defense decided to establish, develop, test, acquire, and deploy a space-borne GPS. The result of this decision is the present NAVSTAR GPS (Navigation Satellite Timing And Ranging Global Positioning System).
Principles of GPS
- The GPS System Consists of 24 Satellite that broadcast Signals containing information about their position and timing.
- A GPS receiver processes signal from at least 4 Satellites.
- GPS system and receiver is the constancy of the speed of light.
GNSS vs GPS
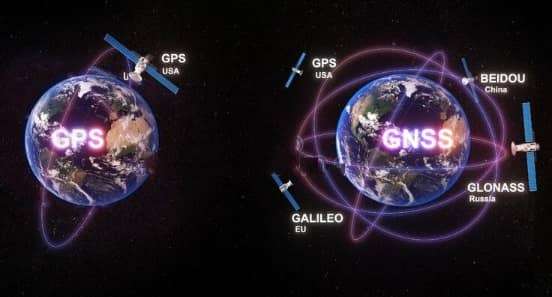
1. Global Navigation Satellite Systems which is referred to as GNSS is a global term that encompasses all of the world’s or global satellite positioning systems
GPS is one of the major components of GNSS and to be more specific it refers to the NAVSTAR Global Positioning System GPOS developed by the USA Department of Defence.
2.GNSS satellite systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galilieo and Beidou.
GPS is one such component under GNSS, introduced by the United State of America.
3.GNSS provides a wider network of satellites that provide better accuracy, availability, and redundancy for every times.
GPS is also having a network of 32 medium earth orbit satellites that are positioned in 6 different orbital planes.
GLONASS
GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System, Russia) is a global GNSS owned and operated by the Russian Federation. The first GLONASS satellite was launched in 1982 and the system was declared fully operational in 1993. The fully operational system consists of 24+ satellites.
GLONASS Satellite Constellation
| Satellites | 24 plus 3 spares |
| Orbital planes | 3 |
| Orbital inclination | 64.8 degrees |
| Orbit radius | 19,140 km |
GLONASS Signal Characteristics
| Designation | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1598.0625 – 1609.3125 MHz | L1 is modulated by the HP (high precision) and the SP (standard precision) signals. |
| L2 | 1242.9375 – 1251.6875 MHz | L2 is modulated by the HP and SP signals. The SP code is identical to that transmitted on L1. |
Galilieo
Galileo is a global GNSS system operated by the European Union. The first Galileo satellites were launched in October 2011, there will be 30 satellites in Medium Earth Orbit at an altitude of 23,222 kilometres.
BeiDou
BeiDou is a global GNSS system, operated by the People’s Republic of China. The first BeiDou satellites were launched in 31 October 2000, operational system consists of 35 satellites. BDS was previously called Compass.
GNSS Receiver
GNSS Receiver is an electronic device that receives data and digitally processes the signals from a navigation satellite constellation in order to provide position, velocity and time.
It has been traditionally implemented in Hardware and Software.

Applications of GNSS
- Location — determining a basic position
- Navigation — getting from one location to another
- Tracking — monitoring the movement of people and things
- Mapping — creating maps of the world or part of it
- Timing — bringing precise timing to the world
Uses of GNSS in GPS
- Almanac Data – The unit stores data about where the satellites are located at any given time. This data is called the almanac.
- Bearing (BRG) – The compass direction from your location to a destination. This is an angular measurement considering the north as 0o.
- Course Made good (CMG) – The bearing from the “active form” position (the starting point) to the present position.
- Cross track Error (XTK) – The distance covered off track from the desired course in either direction.
- Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) – The time of day of arrival at a destination.
- Estimated Time Enroute (ETE) – The time left to reach the destination at the current speed.
- Speed / Velocity Made Good (VMG) – The speed of traveling in the direction of the destination.
- Waypoints – These are the specific points that are recorded by the receiver during a GPS survey.
- Trackpoints –As you travel along, your GPS unit automatically records your journey with some points at a regular interval. These are the trackpoints.
