GIS Data Models
Table of Contents
What is Data Model in GIS?
Data models is a conceptual description of how spatial data are organized for use by the GIS.
Data input involves collecting the necessary data layers into a GIS database.
GIS Data Models
There are two major types of geographic data models ;
- Raster Data Model
- Vector Data Model
Raster Data Model
The Raster model uses regularly spaced grid cells in specfic sequence. An element of the grid cell is called a pixel.
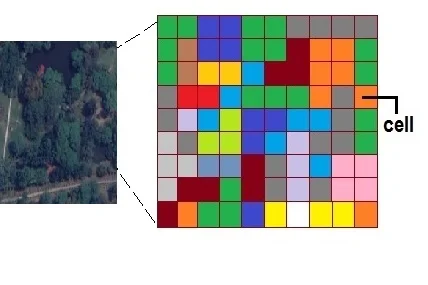
Raster data consists of rows and columns of cells (pixels). In this format a single value is stored against each cell. Raster data can represent a multiplicity of things including:
- Visual images (colour or hue)
- Discrete value, (land use)
- Continuous value, (rainfall)
- Null values if no data is available.
Vector Data Model
The Vector model uses discrete points, lines and areas corresponding to discrete objects with name or code number of attributes.
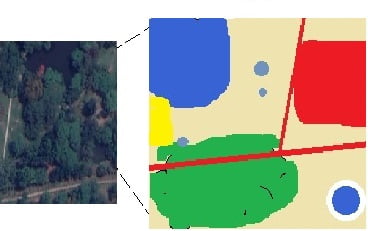
Vector data are graphical objects that have geometrical primitives such as points, lines and polygons to represent geographical entities in the computer graphics.
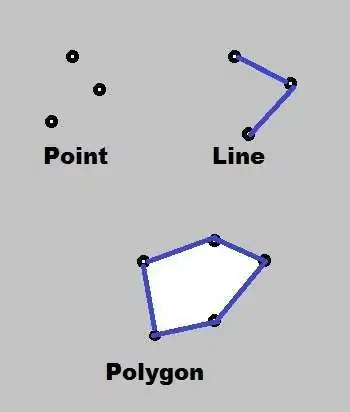
Points, Lines and Polygons can be defined by the coordinate geometry.
- Point- is a ‘0’ dimensional object and has only the property of location (X, Y coordinates – latitude and longitude value). It’s represents building, station, power pole, parks, sample location etc.
- Line (Polyline)- is a one-dimensional object that has the property of length. It’s represent road, streams, oil pipeline, railline, boundary, etc.
- Polygon (Area)- is a two-dimensional object with properties of area and perimeter. It’s represent a city, geologic area, dike, lake, river, etc.