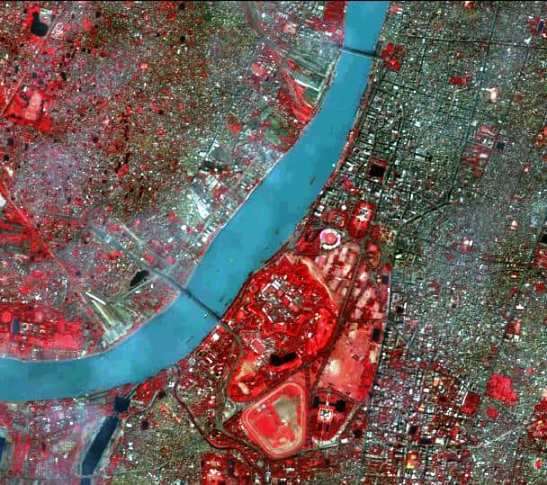
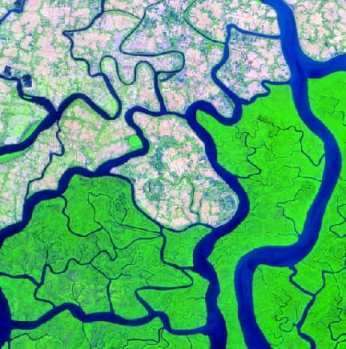
Digital Image Processing in Remote Sensing
A Digital Image is a representation of a two-dimensional image as a finite set of digital values, called picture elements or pixels.
Pixel values typically represent gray levels, colors, heights, opacities etc. Digitization implies that a digital image is an approximation of a real scene.
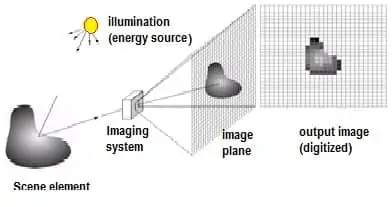
Digital image processing (DIP) focuses on 2 major tasks:
- Improvement of pictorial information for human interpretation
- Processing of image data for storage, transmission and representation for autonomous machine perception
The continuum from image processing to computer vision can be broken up into low-, mid,- and high-level processes
| Low Level Process |
|---|
| Input -Image |
| Output-Image |
| Examples-Image sharpening, Noise removal |
| Mid Level Process |
|---|
| Input-Image |
| Output-Attributes |
| Examples-Segmentation, object recognition |
| High Level Process |
|---|
| Input-Attributes |
| Output-Understandings |
| Examples-Scene understanding, Autonomous navigatiion |
Key Stages in Digital Image Processing
- Image Restoration
- Morphological Processing
- Image Enhancement
- Image Acquisition
- Image Compression
- Segmentation
- Object Recognition
- Representation & Description
- Colour Image Processing