Electromagnetic Spectrum(EMS)
Table of Contents
What is Electromagnetic Spectrum?
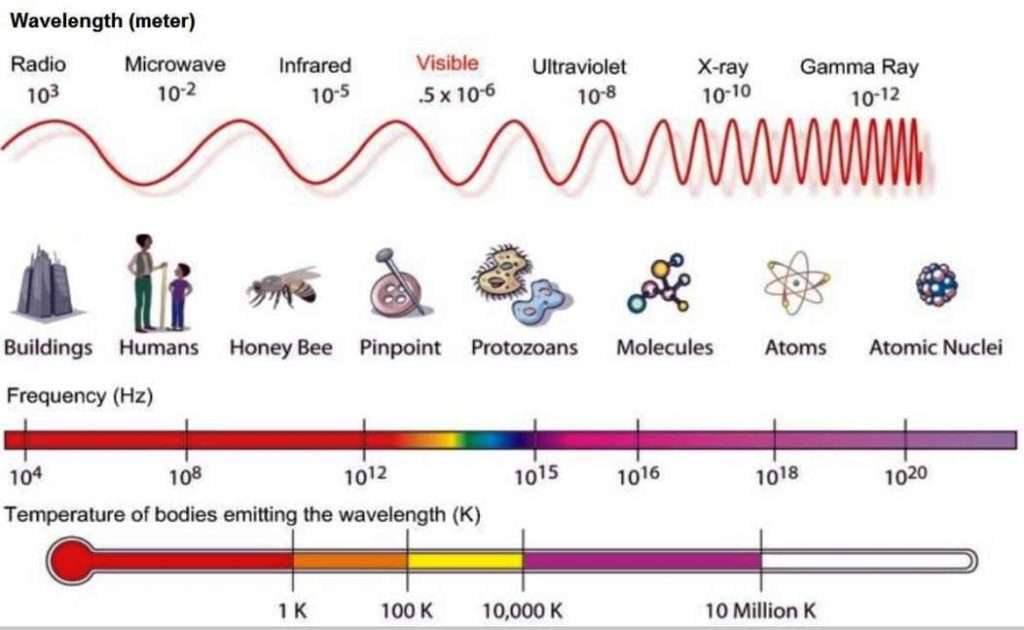
Electromagnetic Spectrum is represented by Electromagnetic waves. It’s characterized by their Wavelength or Frequency, linked by the speed of light. The frequency is associated with energy. High frequency is high energy.
The Electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 10 hertz.
EMS Range of Behavior
The common unit is the electron-volt (eV).
Work done by 1 V potential on 1 electron.
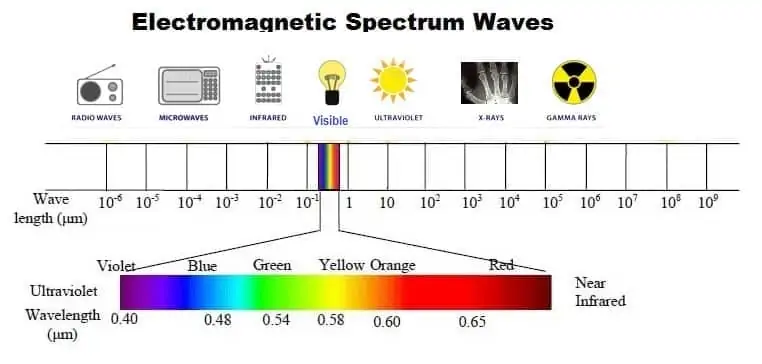
Electromagnetic Spectrum Waves
- Radio waves
- Cell phone waves
- Microwaves
- Radar waves
- Infrared waves
- Visible light waves
- Ultraviolet waves
- X-ray waves
- Gamma waves
| Region | Wavelength (μm) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma rays | < 3×10-5 | Incoming radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere. |
| X-ray | 3×10-5 – 3×10-3 | It is absorbed by atmosphere. |
| Ultraviolet (UV) rays | 0.03 – 0.4 | Wavelengths less than 0.3 are absorbed by the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere. Wavelengths between 0.3- 0.4 μm are transmitted and termed as Photographic UV band. |
| Visible | 0.4 – 0.7 | Able to be discovered or identified with film and photodetectors. |
| Infrared (IR) | 0.7 – 100 | Allows maximum Atmospheric transmission. Portion between 0.7 and 0.9 μm is called photographic IR band, it is detectable with film. Two principal atmospheric windows exist in the thermal IR region between 3 – 5 μm and 8 – 14 μm. |
| Microwave | 103 – 106 | Mark as rain, fog and clouds. Both active and passive remote sensing is possible. Use Radar wavelength in this range. |
| Radio | >106 | Have the longest wavelength. Used for some Radars. |
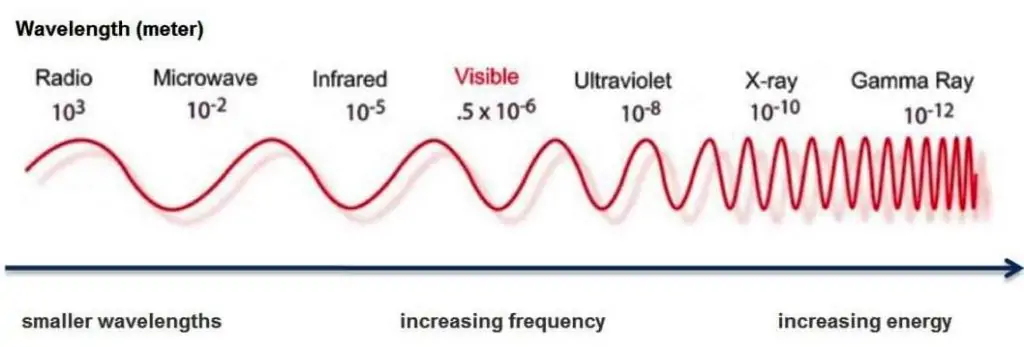
Properties of Electromagnetic waves include: Speed, Frequency and Wavelength.
Speed (s), frequency (f) and wavelength (λ) are related in the formula: is = f x λ
All light waves travel at a speed of 3 x 108 m/s in a vacuum.
Relationship Between Wavelength & Frequency
Wavelength and Frequency have an indirect relationship. That means as wavelength increases, frequency decreases.
Electromagnetic Waves & Energy
High frequency waves have high energy, low frequency waves have low energy.
Radio Waves
Radio waves primarily come from the oscillation of currents in conductors. The long wavelengths travel easily and are not interfered by atoms (Except conductors).
Characteristics of Radio waves
- Low energy waves with the longest wavelengths
- Low frequency
- Includes FM, AM, radar and TV waves
- Wavelengths of 1 m (10 -1 m) and longer
- Used in many devices, such as remote control items, cell phones, wireless devices, etc.
Microwaves
The Microwaves are very short wavelength compared to radio waves. Microwaves are associated with the vibrations of some atoms and molecules. Water molecules act as a dipole.
Characteristics of Microwaves
- Only radio waves are longer
- Wavelength 1 x 10-1 m to 1 x 10-4 m (1 m to 0.001 m)
- Used for communication, medicine and consumer use (microwave ovens)
Infrared Waves
Wavelengths longer than visible light are called Infrared rays. Molecules are heated by infrared waves.
Characteristics of Infrared waves
- Invisible electromagnetic waves that are detected as heat
- Used in heat lamps
- Can be detected with special devices such as night goggles
- Higher energy than microwaves but lower than visible light
The Infra-Red Spectrum
| Wave Division | Wavelength (μm) | Frequency (THz) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Near infra-red | 0.75-1.4 | 214-400 | Atmospheric water absorption |
| Short wave infra-red | 1.4-3 | 100-214 | Atmospheric water absorption increases significantly at 1.45 um. 1.53 to 1.56 um is used in long distance communication |
| Medium wave infra-red | 3-8 | 37-100 | Heat seeking missiles are designed to work in this spectrum |
| Long wave infra-red | 8-15 | 20-37 | Thermal imaging region |
Visible Light
Visible light is radiation in a narrow band of wavelength. Many atoms and molecules have specific behavior at unique frequencies of light. Corresponds to maximum output from the Sun.
Characteristics of Visible Light
- Narrower ranges are colors (400 nm to 800 nm)
- The portion of the Electromagnetic spectrum that human eyes can detect.
- Visible Light- ROY G BIV (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet)
- Red has the lowest frequency, violet is the highest
Ultraviolet Waves
Ultraviolet rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light. Some molecules absorb ultraviolet and remit visible light.
Characteristics of Ultraviolet
- Higher energy than light waves
- Can cause skin cancer and blindness in humans
- Used in tanning beds and sterilizing equipment
X-Rays
X-rays are associated with energetic transitions in atoms. The short wavelength x-rays can penetrate materials.
Characteristics of X-rays
- High energy waves
- Continuous spectra result from electron bombardment
- Used in medicine, industry and astronomy
- Can cause cancer
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are photons associated with nuclear or particle processes. Acceleration of a very energetic charged particle gives x-rays and gamma rays, it’s Called bremsstrahlung.
Characteristics of Gamma rays
- The highest energy
- Energy range overlaps, soft gamma equals hard x-ray
- Blocked from Earth’s surface by Atmosphere
