Navigation Satellites
Satellites navigation services to meet the emerging demands of the Civil Aviation requirements and to meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation and timing based on the independent satellite navigation systems.
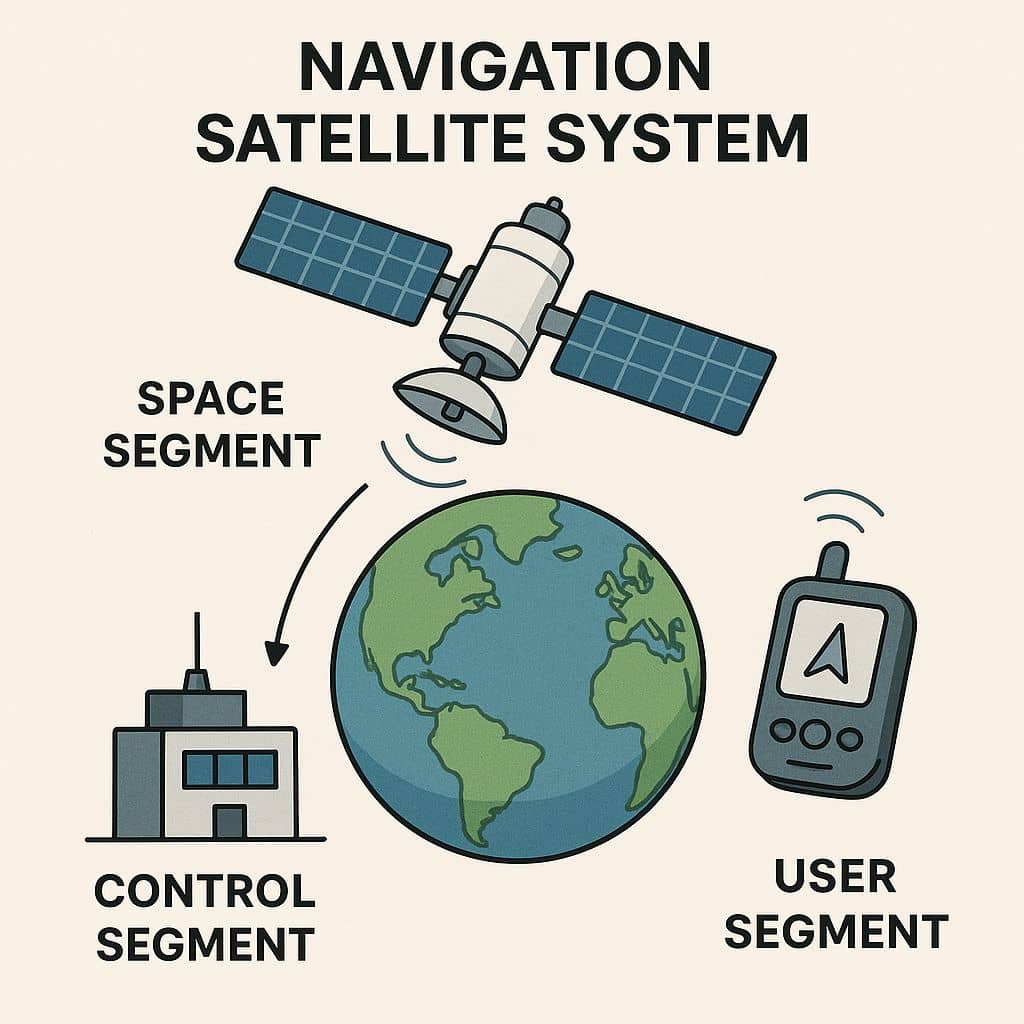
Satellite Navigation Systems is based on a global network of satellites that transmit radio signals from medium earth orbit.
Satellite Navigation with the 31 Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites developed and operated by the United States.
While GPS is the most prevalent GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System). GNSS can also refer to augmentation systems, but there are too many international augmentations to list below:
How It Works
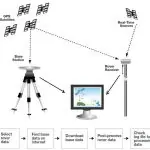
- Signal Transmission – Satellites continuously transmit time-stamped radio signals.
- Signal Reception – A GPS receiver picks up signals from at least four satellites.
- Trilateration – The receiver calculates the distance from each satellite and determines the user’s 3D position (latitude, longitude, altitude) and time.
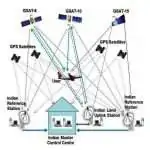
Indian Navigation Satellite
ISRO is working jointly with Airport Authority of India (AAI) in establishing the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system. To meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation and timing services based on the indigenous system, ISRO is establishing a regional satellite navigation system called Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation (GAGAN)
GAGAN is a Satellite Based Augmentation System implemented jointly with Airport Authority of India (AAI).
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS): NavIC
IRNSS is an independent Indian Satellite based positioning system for critical National applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ High accuracy (typically 5–10 meters; better with augmentation) ✅ Available worldwide, 24/7 ✅ Works in all weather conditions | ❎ Signal blockage in tunnels, deep forests, or urban canyons ❎ Vulnerable to jamming and spoofing ❎ Requires line-of-sight to satellites |