Overview of QGIS: The Free and Open-Source GIS Platform
What is QGIS?
QGIS stand for Quantum GIS, it’s a Free and open-source GIS Software to perform GIS (Geographic Information System) application, that supports create, edit, visualize and analysis of Geo-spatial data.
Uses of QGIS:
- Mapping & Cartography
- Designing thematic maps with legends, scale bars, and labels.
- Spatial Analysis
- Buffering, overlay, proximity, terrain, and hydrology analysis.
- Remote Sensing
- Image classification, NDVI calculation, and band combination.
- Data Management
- Editing shapefiles, digitizing maps, and managing GeoPackages.
- Web GIS
- Publishing maps via QGIS Server or integrating with Leaflet/Mapbox.
Download QGIS Software
The current version is of QGIS 3.44.0 ‘Solothurn’ has been released. Download QGIS Software.
Core Components of QGIS
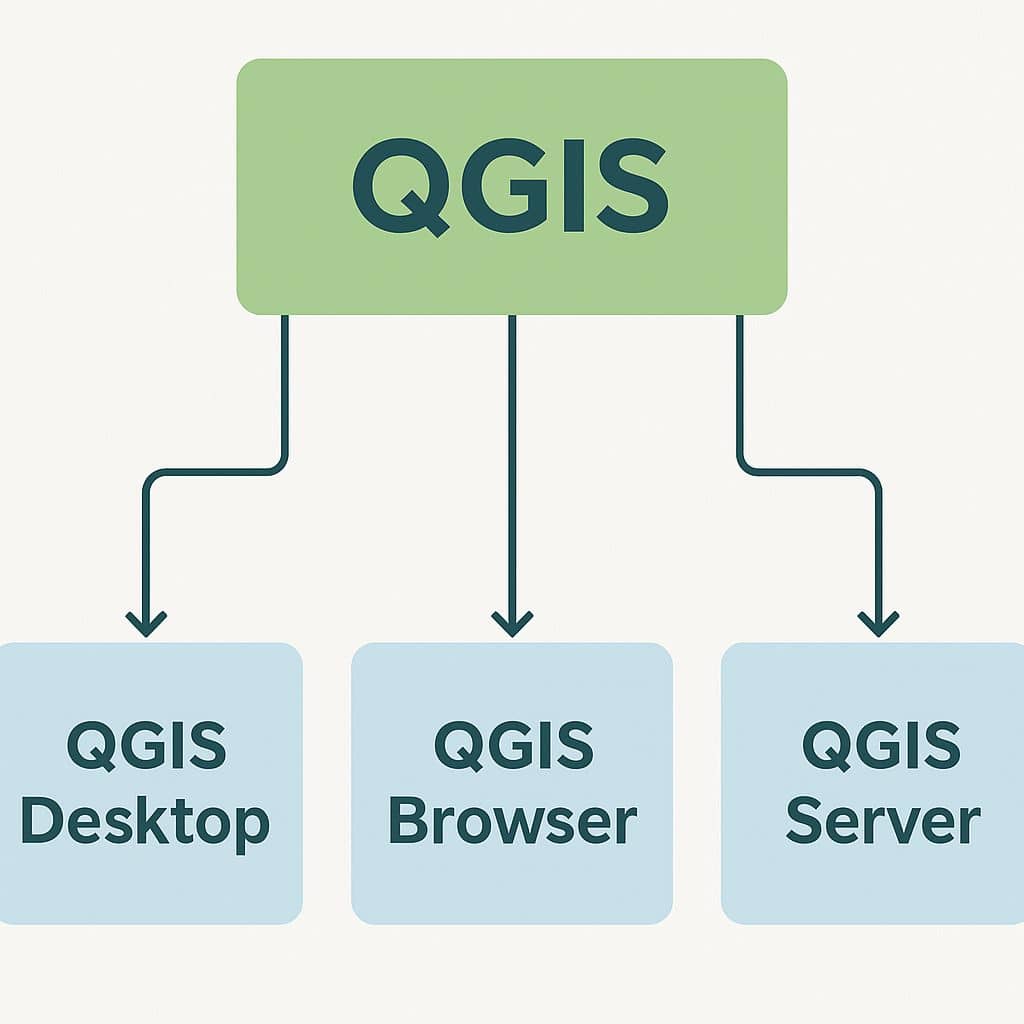
- QGIS Desktop: Main interface for map creation, analysis, and visualization.
- QGIS Browser: Quick access to data and file management.
- QGIS Server: Publish maps and data as web services (WMS/WFS/WCS).
- QGIS Web Client (QWC2): A web mapping front-end for published data.
- QField for QGIS: Mobile data collection and field mapping app.
QGIS Desktop
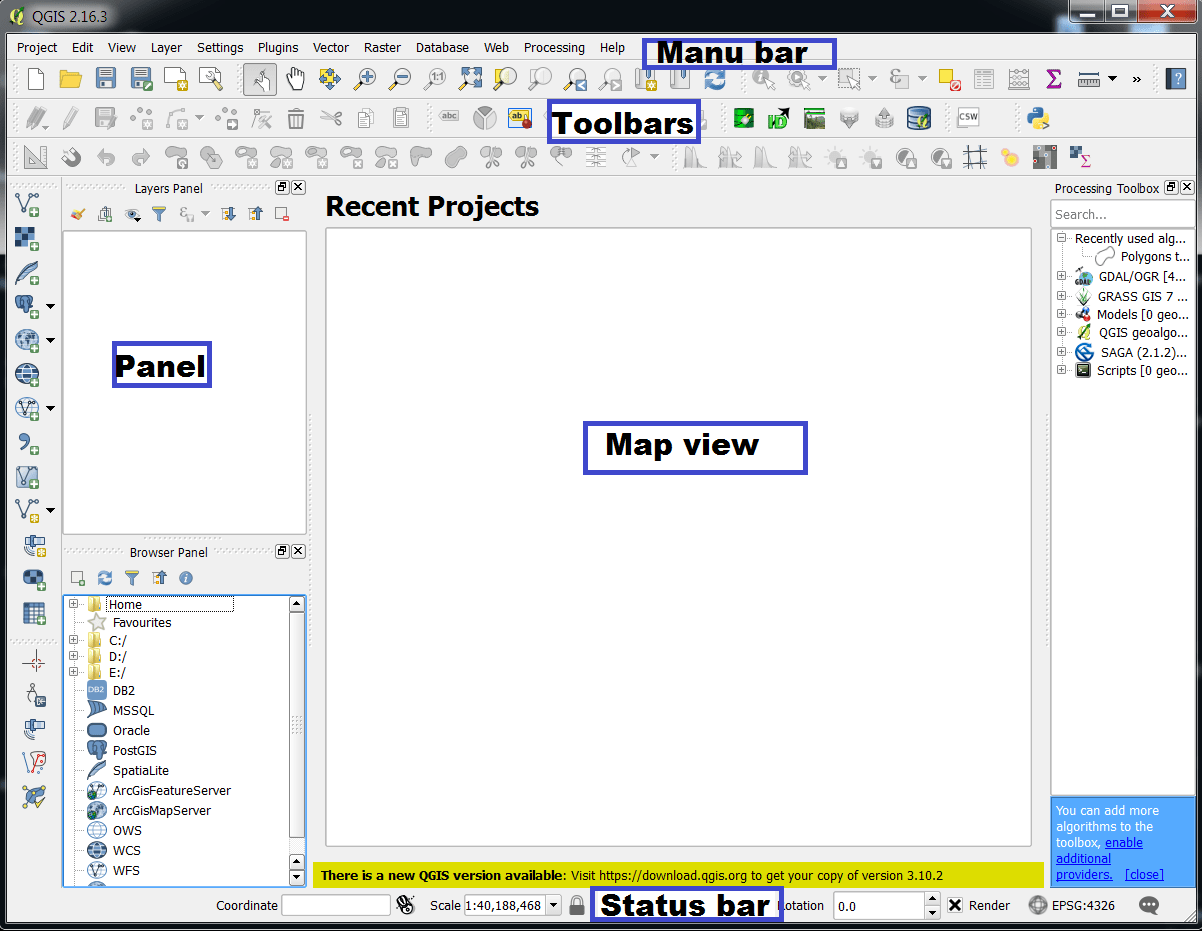
The QGIS GUI (Graphical User Interface) is divided into five components:
- Menu Bar
- Toolbars
- Panels
- Map View
- Status Bar
Panel & Toolbars
QGIS Menu Bar
The Menu Bar is located at the top of the QGIS interface and provides access to all major tools and functionalities organized into menus.
1. Project
- New / Open / Save Project
- Import/Export Project
- Project Properties (CRS, metadata)
- Exit
2. Edit
- Cut / Copy / Paste features
- Undo / Redo
- Edit geometry (Add, Delete vertex)
- Snapping options
3. View
- Pan / Zoom in-out / Full extent
- Map navigation tools
- Show/Hide panels and toolbars
- Decorations (Scale bar, North arrow, Grid)
4. Layer
- Add Vector, Raster, Mesh, Point Cloud layers
- Create/Edit Layers (Shapefile, GeoPackage)
- Layer Properties & Styling
- Group layers or create virtual layers
5. Settings
- Options (General, CRS, Digitizing, Network)
- Style Manager
- Configure shortcuts and toolbars
6. Plugins
- Manage and install plugins
- Python plugin console
- Access external tools like QuickMapServices
7. Vector
- Geoprocessing tools: Buffer, Clip, Dissolve
- Geometry and attribute tools
- Analysis tools (Join, Count, Sum)
8. Raster
- Raster calculator
- Terrain analysis (Slope, Aspect, Hillshade)
- Conversion tools (Raster to Vector)
9. Database
- Connect to PostGIS, SpatiaLite, MSSQL, Oracle
- Run SQL queries
- Import/export tables and layers
10. Web
- Access online services (WMS, WFS, XYZ Tiles)
- Connect to OpenStreetMap or external map services
11. Mesh
- Tools for 3D or scientific grid data
12. Processing
- Open Processing Toolbox (integrates SAGA, GRASS, GDAL)
13. Help
- Documentation, shortcuts, About QGIS
QGIS Panels and Toolbars
Panels
| Panel name | Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Advanced Digitizing | Ctrl+4 |
| Browser | Ctrl+2 |
| Browser (2) | |
| Debugging/Development Tools | F12 |
| Elevation Profile | |
| Geometry Validation | |
| GPS Information | Ctrl+0 |
| GRASS Tools | |
| Layer Order | Ctrl+9 |
| Layer Styling | Ctrl+3 |
| Layers | Ctrl+1 |
| Log Messages | |
| Overview | Ctrl+8 |
| Processing Toolbox | |
| Results Viewer | |
| Snapping and Digitizing Options | |
| Spatial Bookmark Manager | Ctrl+7 |
| Statistics | Ctrl+6 |
| Temporal Controller | |
| Tile Scale | |
| Undo/Redo | Ctrl+5 |
| Vertex Editor |
Toolbars
| Toolbar Name |
|---|
| Advanced Digitizing Toolbar |
| Annotations Toolbar |
| Attributes |
| Data Source Manager |
| Database |
| Digitizing |
| Help |
| Label |
| Manage Layers |
| Map Navigation |
| Mesh Digitizing Toolbar |
| Plugins |
| Project |
| Processing Algorithms |
| Raster |
| Selection |
| Shape digitizing |
| Snapping |
| Vector |
| Web |
QGIS Map View
| Map view Options |
|---|
| Exploring the map view |
| Setting additional map views |
| Exporting the map view |
QGIS Status Bar
| Status bar Options |
|---|
| Locator bar |
| Reporting actions |
| Control the map canvas |
| Messaging |
QGIS Default Core Plugins
| Plugin | Description |
|---|---|
| DB Manager | Manage your databases |
| Geometry Checker | Check and repair errors in vector geometries |
| GPS Tools | Tools for loading and importing GPS data |
| GRASS | GRASS functionality |
| MetaSearch Catalog Client | Interact with metadata catalog services (CSW) |
| Offline Editing Plugin | Offline editing and synchronizing with database |
| Processing framework | Spatial data processing framework |
| Topology Checker | Find topological errors in vector layers |
QGIS Raster Properties
QGIS Software Tutorial
Georeferencing
The Georeferencer tool generating reference raster to geographic or projected coordinate systems by creating a new GeoTIff or by adding a world file to the existing image.
Perform Image to Image Georeferencing.
Perform Ground to Image Georeferencing.
Vector Data (Shapefile)
The Vector file or Shapefile is digital forms of maps to create symbology, labeling, diagrams. It also data storage format for storing the location, shape, and attributes of geographic features.
Create Vector Data or Shapefile.
Digitization
Digitization is a process of Raster 2 Vector Conversion.
Perform Raster 2 Vector Conversion (screen Digitization).
Uses of Attributes Toolbar
Attributes Toolbar use for editing Maps and manipulating Data.
Use Attributes Toolbar.
Layout (Print composer)
The Print Composer provides growing layout and printing capabilities. It allows you to add elements such as the Q-GIS map canvas.
Perform Layout in QGIS.
FAQ?
Q-GIS is the Free and Open Source Desktop GIS Software. It allows you to create, edit, visualize, analyze and publish Geo-spatial information.
Q-GIS is available on Windows, macOS, Linux and Android.
The current version is Q-GIS 3.32.3 ‘Lima’ has been released. Download QGIS Software.
QGIS is the easiest for learning. Many sources are to learn Q-GIS. Free QGIS Tutorial for Beginners is available in GISRSSTUDY.