Raster Processing- Layer stack, Subset and Mosaic, using Erdas Imagine
Raster Image Processing is the enhancement and analysis of raster data—commonly used in Remote Sensing, GIS, and Digital Image Processing. Raster processing is crucial because most satellite images, aerial photos, DEMs, and climate datasets are in raster format.
A Raster image processor is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a Bitmap.
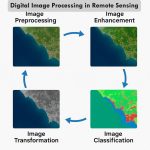
Steps of Raster Image Processing in Remote Sensing
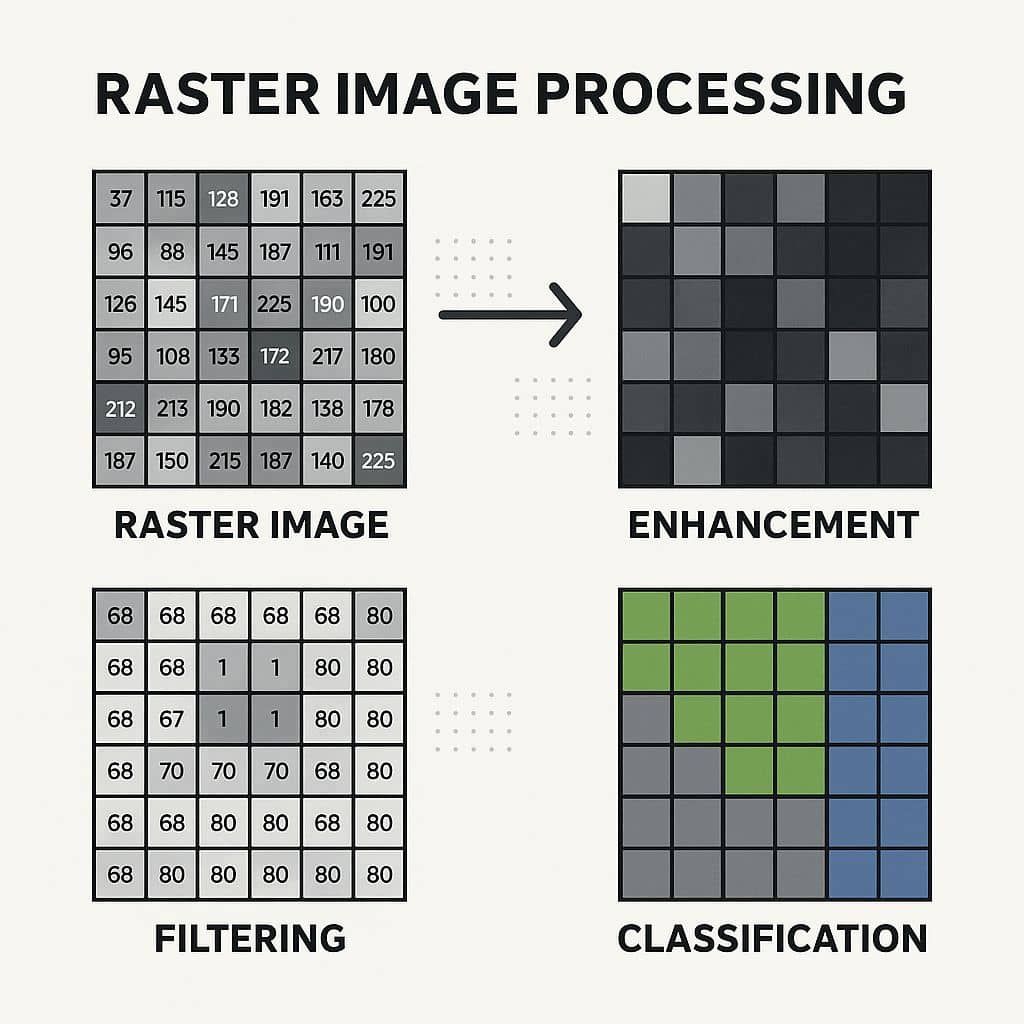
Raster image processing can be divided into three main stages:
A. Raster Preprocessing
Prepares raw raster data for analysis.
- Geometric Correction
- Align the raster to a coordinate system (Georeferencing).
- Example: Correcting Landsat image to match GPS points.
- Radiometric Correction
- Adjust pixel values to remove sensor or atmospheric effects.
- Example: Atmospheric correction to improve NDVI accuracy.
- Resampling
- Change the spatial resolution of the raster (Nearest Neighbor, Bilinear, Cubic).
B. Raster Enhancement
Improves the visual quality or interpretability of the raster.
- Contrast Stretching / Histogram Equalization
Highlights features in satellite imagery. - Spatial Filtering
- Low-pass filter (smoothing) → Removes noise.
- High-pass filter (edge enhancement) → Highlights roads or boundaries.
- Band Combinations (False Color Composite)
Combine multiple bands to highlight vegetation, water, or urban areas.
C. Raster Analysis
Extracts meaningful information from raster data.
- Raster Classification
- Supervised (uses training data)
- Unsupervised (clusters pixels automatically)
- Raster Algebra (Map Algebra)
- Apply mathematical operations between raster layers.
- Example: NDVI = (NIR – Red) / (NIR + Red)
- Raster to Vector Conversion
- Convert classified raster to polygons for GIS analysis.
- Zonal and Statistical Analysis
- Summarize raster values by administrative boundaries or regions.
- Raster Overlay Analysis
- Combine multiple raster layers (e.g., slope + rainfall for flood risk).
Raster Image Processing Method
In this Tutorial, explain and create three Raster image processing method using Erdas Imagine software.
- Layer stack
- Subset
- Mosaic
Layer stack
Layer stack is one of the useful Raster image processing method. It is a process of join a single Band.
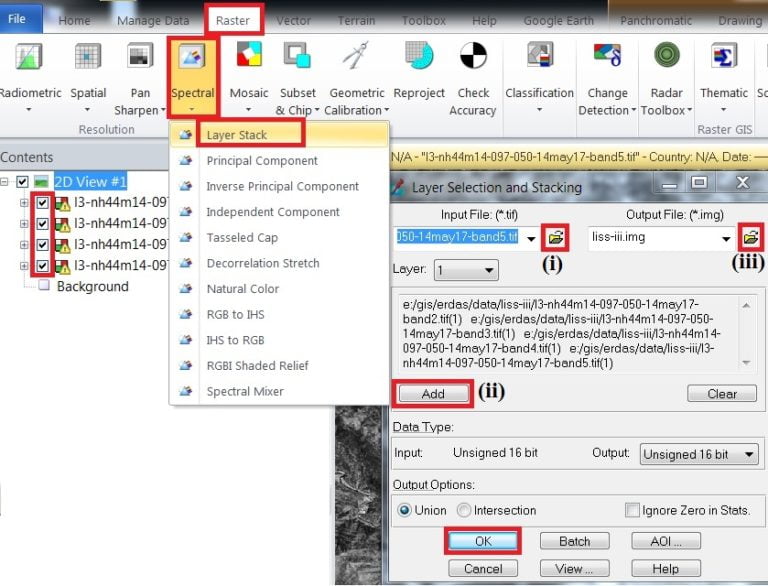
1. On the Raster tab, click Spectral and select Layer stack.
2. Layer stack window is appears, Browse Input file (i) and Add (ii) one by one layer. Add all the single Bands, now select Output file (iii) and click OK.
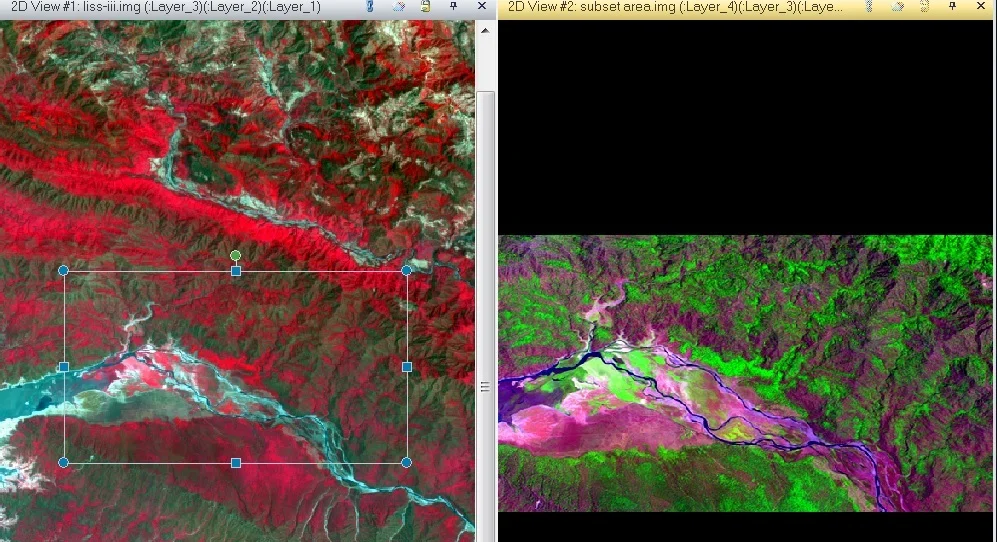
Subset
Subset is a process of the Slip method as well as extract image.
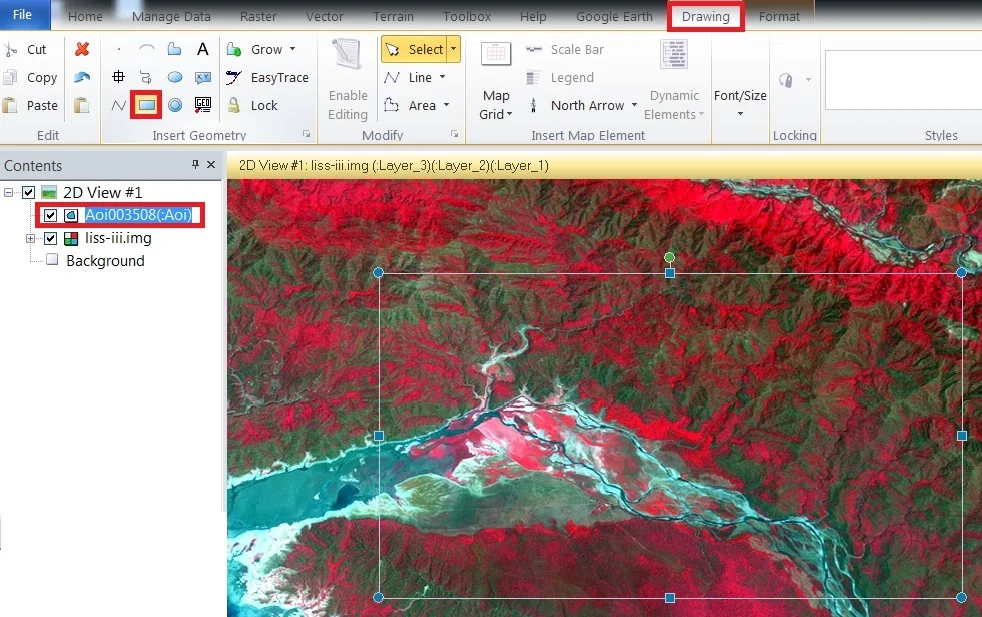
AOI (Area of Interest)
First, select the area, perform to the subset.
1. On the Draw tab, Insert Geometry group Rectangle and Drag it in your map.
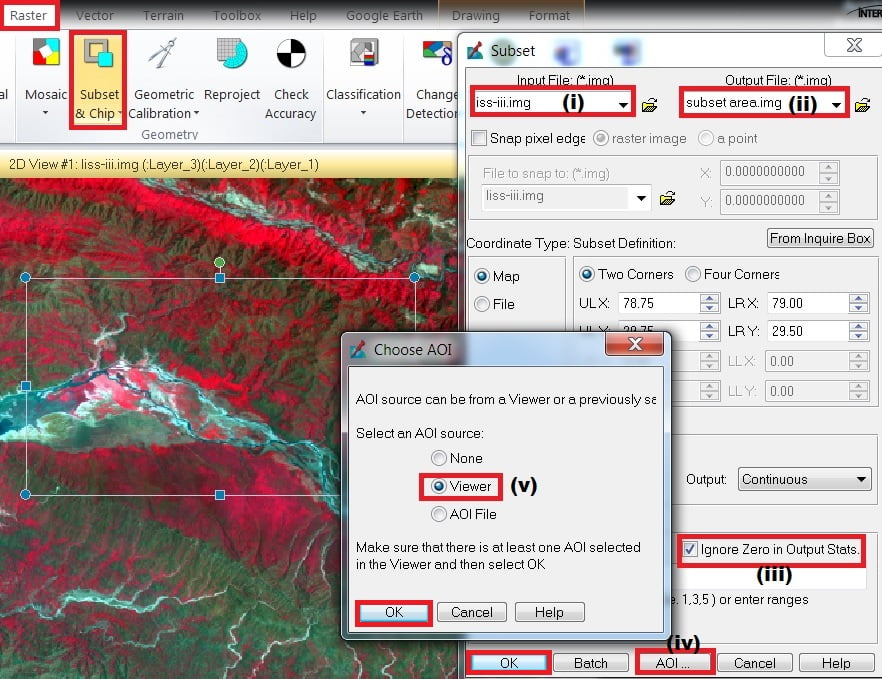
2. On the Raster tab, select Subset & chip and click create Subset image.
3. Subset pane are open, select Input file(i) and Output file (ii), check into ignore zero in output stats (iii), then click AOI (iv) button. Choose an AOI window is appears, choose Viewer (v) and click OK, then click OK
Mosaic
Mosaic describe, join two or multiple Geographic path images.
1. On the Raster tab, select Mosaic and click MosaicPro
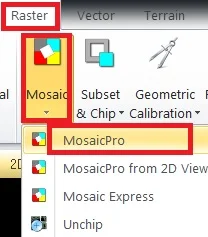
2. MosaicPro pane are appears, click Display, add images dialog (i) and choose the images. The images are added now visible the images, just check into the box (ii) and click Display Raster images (iii).
3.Select Automatically generate seamlines for intersection (iv), seamlines generation options pane is open, choose Weighted seamlines and click OK.
4. Now select set overlap/seamline function(fx) (v), set seamline function pane is open, choose Smoothing and Feathering and click OK button.
5. All the Task is complete, click Run the Mosaic process to disk (vi).
Applications
- Land Use / Land Cover Mapping
- Agricultural Monitoring (NDVI, Crop Health)
- Hydrology and Watershed Analysis
- Disaster Management (Flood, Landslide, Fire mapping)
- Climate and Environmental Studies

very Intersting Sebject
Thanks
I want to ask how to rotate my map image because in the first open,the image in landskap but i want in portrait…can you tell me how to rotate the map??
please tell us, which software you use?
Erdas imagine 2014
In Scale & Angle panel, use Angle option.
