Spatial Data Models in GIS
In Geographic Information Systems (GIS), spatial data models serve as a framework for digitally representing the real world. It defines how different elements of geographic information are structured, stored, and related to each other within a GIS database. These models capture the geometry (e.g., shape, location) and attributes (e.g., name, type, value) of features on the Earth’s surface.
Components:
- Spatial data: Geometry (shape and location)
- Attribute data: Descriptive information
- Topology: Spatial relationships (e.g., adjacency, connectivity)
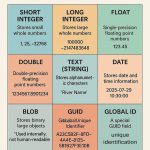
- Metadata: Data about data (source, accuracy, etc.)
GIS Data Models
GIS Data is primarily categorized into two formats:
- Raster Data Model
- Vector Data Model
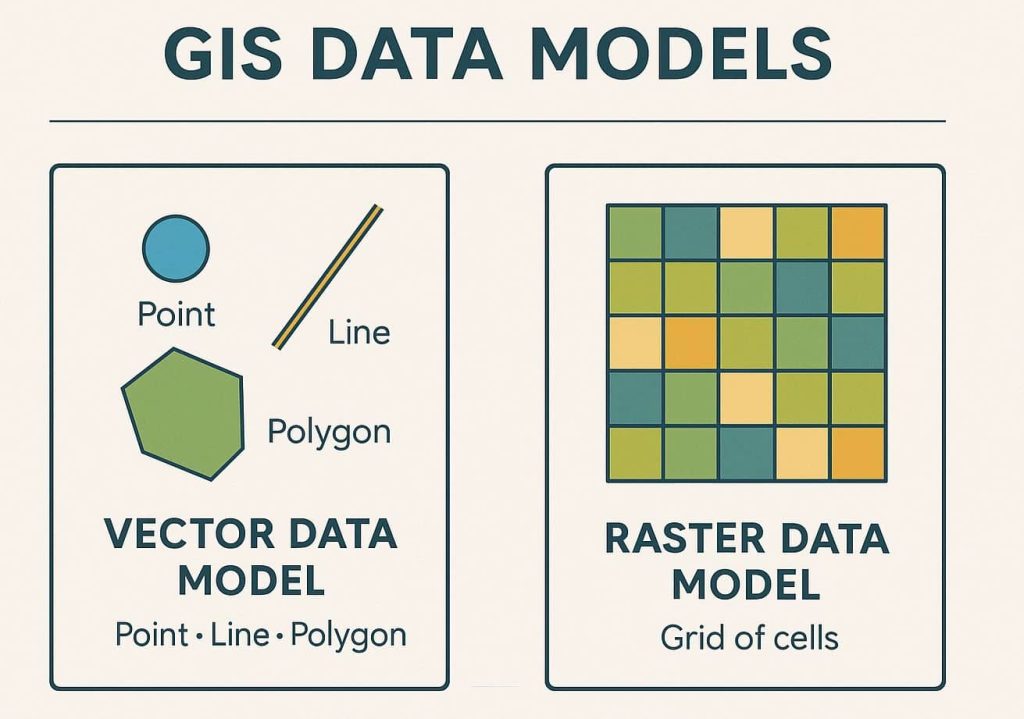
Raster Data Model
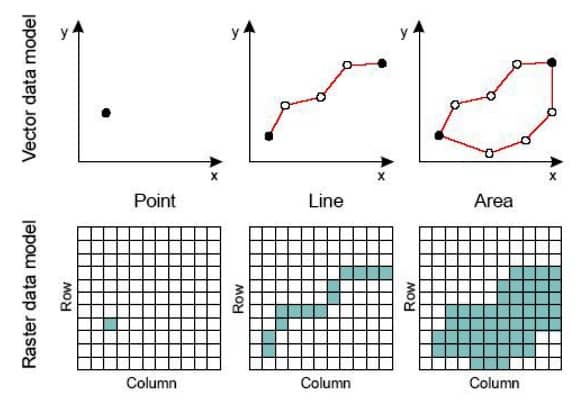
The Raster Data Model represents the world as a surface divided into a grid of equally sized cells (pixels). Each cell contains a value representing a specific attribute such as elevation, temperature, or land cover.
Raster Data consists of rows and columns of cells (pixels). In this format a single value is stored against each cell. Raster data can represent a multiplicity of things including:
- Visual images (colour or hue)
- Discrete value, (land use)
- Continuous value, (rainfall)
- Null values if no data is available.
Vector Data Model
The Vector Data Model uses points, lines, and polygons to represent spatial features. It is ideal for mapping features with discrete boundaries such as roads, political borders, and buildings. The selection of a point, line, or polygon in a map depends on the theme and scale of the map.
Vector Data are graphical objects that have geometrical primitives such as points, lines and polygons to represent geographical entities in the computer graphics.
Points, Lines and Polygons can be defined by the coordinate geometry.
- Point- is a ‘0’ dimensional object and has only the property of location (X, Y coordinates – latitude and longitude value). It’s represents building, station, power pole, parks, sample location etc.
- Line (Polyline)- is a one-dimensional object that has the property of length. It’s represent road, streams, oil pipeline, railline, boundary, etc.
- Polygon (Area)- is a two-dimensional object with properties of area and perimeter. It’s represent a city, geologic area, dike, lake, river, etc.
Other GIS Data Model
TIN (Triangulated Irregular Network)
- Represents surface using interconnected triangles
- Good for elevation modeling
Object-Based Data Model
- Treats features as intelligent objects with behaviors and rules (used in modern GIS and geodatabases)
Geodatabase Model
- An advanced ESRI-specific data model
- Stores vector, raster, topology, relationships, and metadata in one container