Remote Sensing Soil Moisture
Soil is basically a layer of unconsolidated material found at the Earth’s surface that has been influenced by the soil forming factors.
The moisture content of soil depends on such factors as weather, type of land, and plants. The soil moisture content in the surface layers is an important parameter for many applications in hydrology, agriculture and meteorology. Soil moisture is one of the few directly observable hydrological variables that play an important role in the water and energy budgets necessary for climate studies.
Soil moisture affects:
- content of air, salinity, and amount of toxic substances
- ground structure and thickness
- temperature and heat capacity of the ground
Remote sensing of soil moisture content has been studied and developed over two decade. Soil moisture estimation by means of remote sensing depends upon the measurements of electromagnetic energy that has either been reflected or emitted from the soil surface.
Soil Moisture Indices – Erdas Imagine
In this tutorial perform three types of Soil Indices; Sundarbans Landsat TM Satellite image.
Perform Clay Minerals
At first open Indices window; on the main menu, select Raster > dropdown Unsupervised section > click Indices.
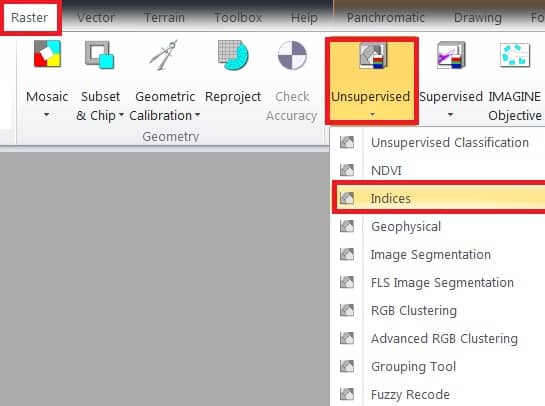
1. Now indices window is appeared, select Input file (ex.- sundarbans), then go to destination folder and enter Output file name.
2. Choose your satellite data Sensor (ex.- Landsat 4 TM).
3. In the Index section, choose your query- CLAY MINERALS.
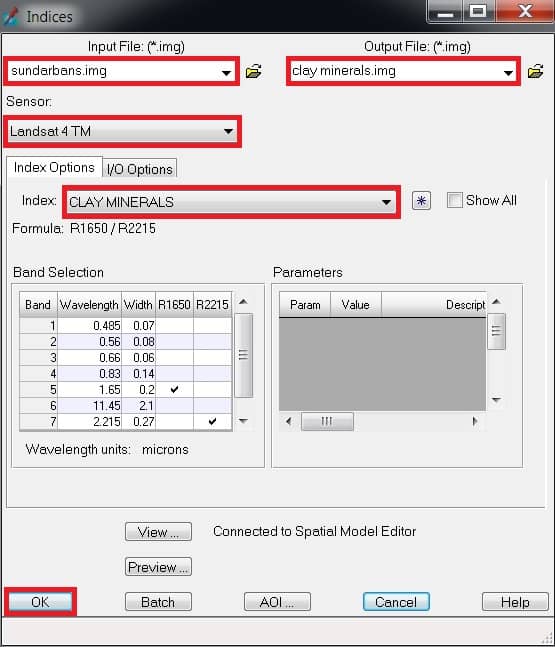
4. Finally click OK button.
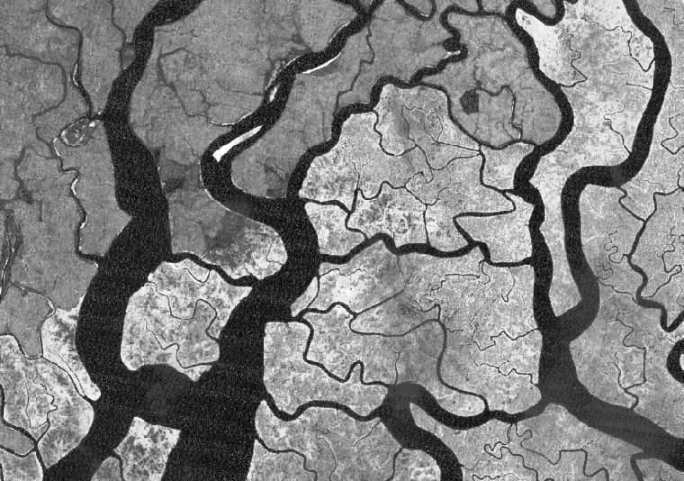
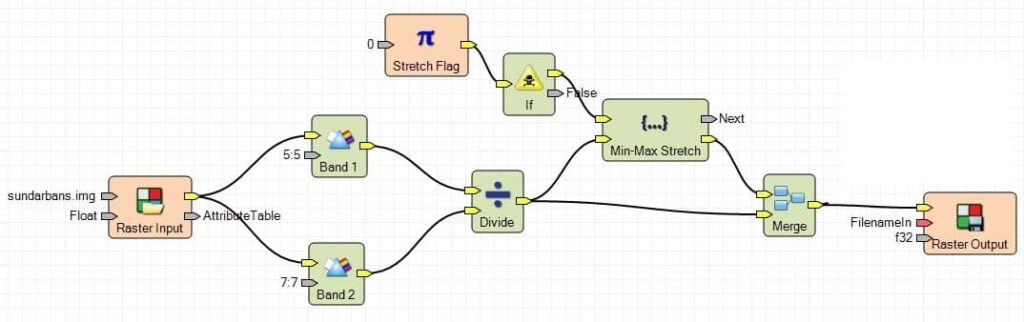

Perform Moisture Stress Index
1. Once you have already open indices window, select Input file (ex.- sundarbans), then go to destination folder and enter Output file name.
2. Choose your satellite data Sensor (ex.- Landsat 4 TM).
3. In the Index section, choose Moisture Stress Index.
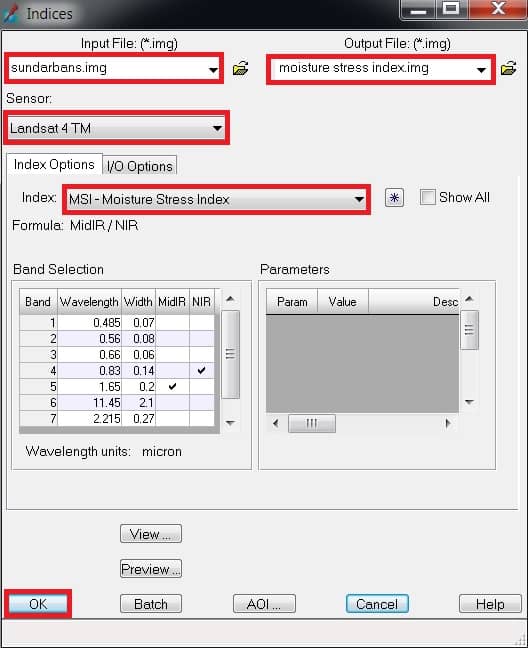
4. Finally click OK button.
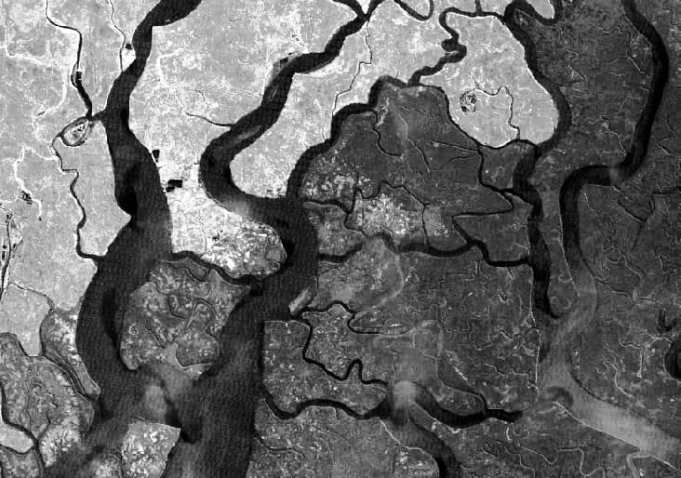

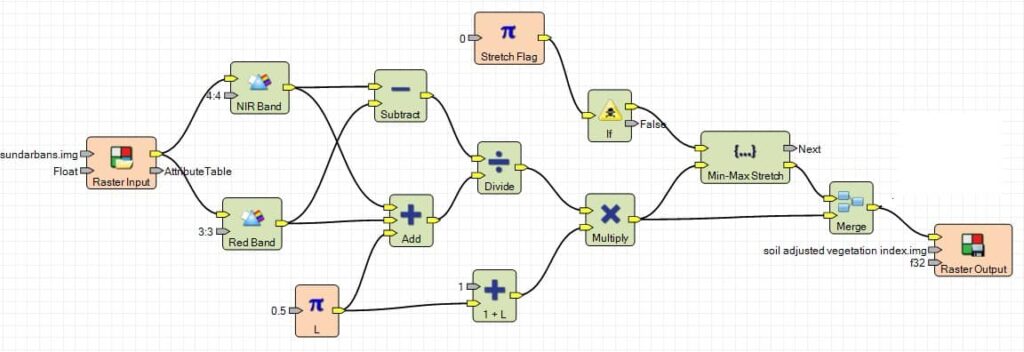
Perform Soil Adjusted Vegetation
1. Once you have already open indices window, select Input file (ex.- sundarbans), then go to destination folder and enter Output file name.
2. Choose your satellite data Sensor (ex.- Landsat 4 TM).
3. In the Index section, choose Soil Adjusted Vegetation.
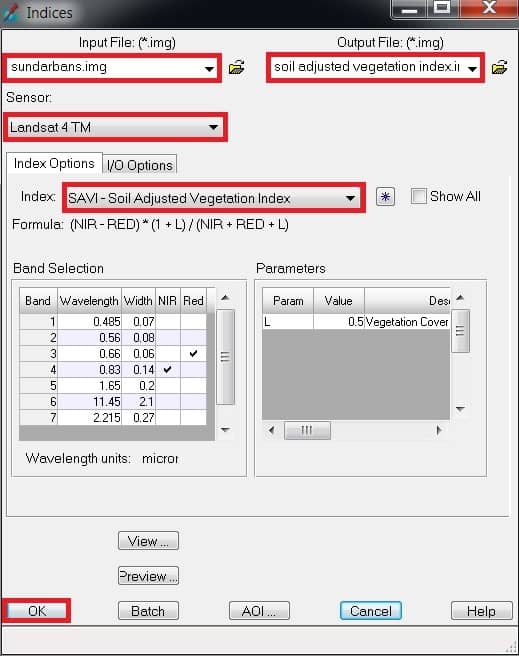
4. Finally click OK button.