Digital Image Processing: Remote Sensing
A Digital Image is a representation of a two-dimensional image as a finite set of digital values, called picture elements or pixels.
Pixel values typically represent gray levels, colors, heights, opacities etc. Digitization implies that a digital image is an approximation of a real scene.
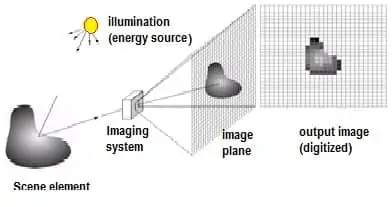
Digital image processing (DIP) focuses on 2 major tasks:
- Improvement of pictorial information for human interpretation
- Processing of image data for storage, transmission and representation for autonomous machine perception
The continuum from image processing to computer vision can be broken up into low-, mid,- and high-level processes
| Low Level Process |
|---|
| Input– Image |
| Output– Image |
| Examples– Image sharpening, Noise removal |
| Mid Level Process |
|---|
| Input– Image |
| Output– Attributes |
| Examples– Segmentation, object recognition |
| High Level Process |
|---|
| Input– Attributes |
| Output– Understandings |
| Examples– Scene understanding, Autonomous navigation |
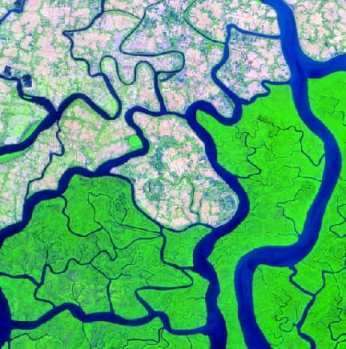
What is Digital Image Processing in Remote Sensing
Digital Image Processing (DIP) in Remote Sensing is the application of image processing techniques to satellite or aerial imagery to extract meaningful information about the Earth’s surface. This is a core part of GIS and Remote Sensing workflows because raw satellite images are often affected by distortions and require processing before analysis.
DIP in remote sensing helps to:
- Enhance image quality
- Correct distortions
- Extract thematic information (like vegetation, water bodies, urban areas)
Key Stages in Digital Image Processing
- Image Restoration
- Morphological Processing
- Image Enhancement
- Image Acquisition
- Image Compression
- Segmentation
- Object Recognition
- Representation & Description
- Colour Image Processing
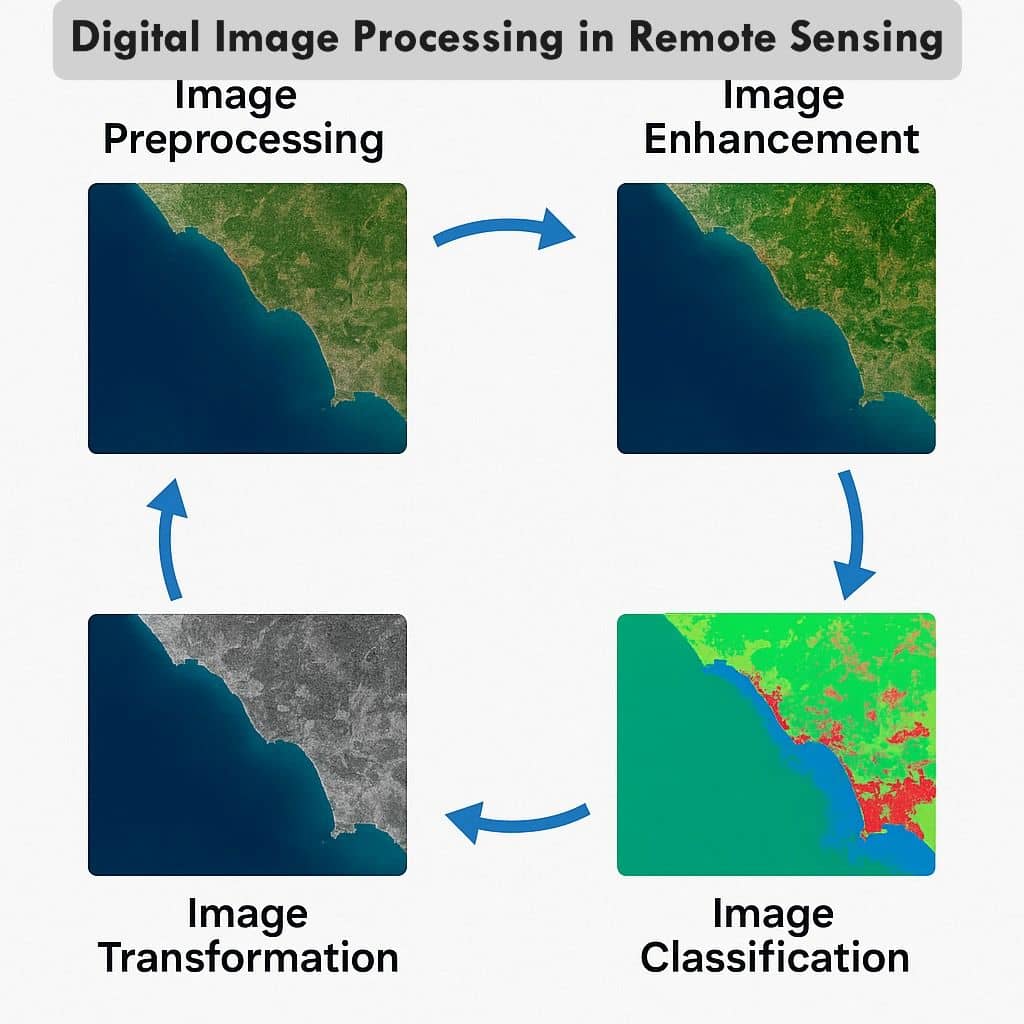
Steps of Digital Image Processing in Remote Sensing
A. Image Preprocessing
Preprocessing improves image quality and prepares it for analysis.
- Radiometric Correction
- Corrects sensor or atmospheric errors (haze, striping).
- Example: Dark object subtraction for haze correction.
- Geometric Correction
- Aligns the image to real-world coordinates.
- Example: Georeferencing using Ground Control Points (GCPs).
- Atmospheric Correction
- Removes scattering and absorption effects caused by the atmosphere.
- Example: Using FLAASH or QUAC in ENVI.
B. Image Enhancement
Used to make features more interpretable to the human eye or for automated analysis.
- Contrast Stretching: Improves visibility of features.
- Histogram Equalization: Enhances brightness distribution.
- Spatial Filtering:
- Low-pass filter → smooths image
- High-pass filter → enhances edges or boundaries
C. Image Transformation
Transforms raw spectral bands into meaningful indices or components:
- Vegetation Indices
- Example: NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) to identify healthy vegetation.
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Reduces data dimensionality and highlights important features.
- Tasseled Cap Transformation
- Highlights soil, vegetation, and moisture characteristics.
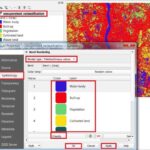
D. Image Classification
Converts images into thematic maps by assigning land-cover classes.
- Supervised Classification
- Uses training samples (known land cover types).
- Algorithms: Maximum Likelihood, Support Vector Machine (SVM).
- Unsupervised Classification
- Groups pixels based on spectral similarity without prior knowledge.
- Algorithm: ISODATA, K-means.
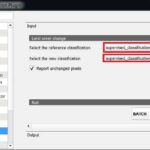
E. Post-Classification Processing
- Accuracy Assessment: Comparing classified results with ground truth.
- Change Detection: Identifying differences between images from different times (useful for deforestation or urban growth studies).
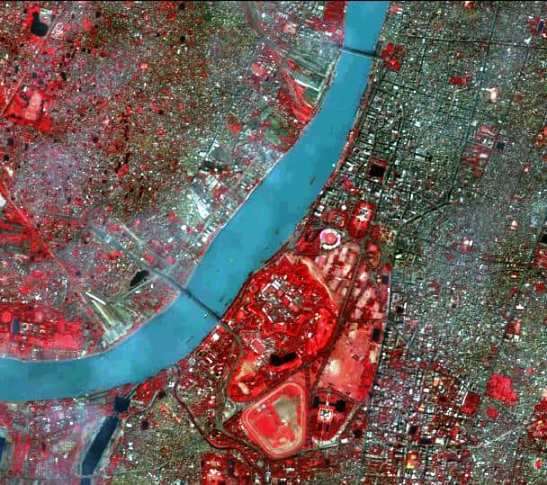
Image Processing Examples
Applications
Digital image processing in remote sensing is used in:
- Land Use/Land Cover Mapping
- Identify urban areas, forests, agriculture, and water bodies.
- Agriculture and Crop Monitoring
- NDVI for crop health and yield prediction.
- Disaster Management
- Flood extent mapping, wildfire burn area detection.
- Environmental Monitoring
- Deforestation, soil erosion, and wetland assessment.
- Urban Planning