kriging in ArcGIS
Kriging in ArcGIS is a powerful geostatistical interpolation technique used to predict values at unmeasured locations based on known point data. It’s available primarily through the Geostatistical Analyst extension in ArcMap and ArcGIS Pro.
What is Kriging?
Kriging is an advanced geostatistical procedure that generates an estimated surface from a scattered set of points with z-values.?
An Kriging assumes the distance or direction between sample points reflects a spatial correlation that can be used to explain variation in the surface.
The Kriging tool fits a mathematical function to a specified number of points, it is a multistep process, includes exploratory statistical analysis of the data, variogram modeling, creating the surface, and exploring a variance surface.
Kriging Methods–
There are two kriging methods:
- Ordinary kriging– is the most general and widely used of the kriging methods and is the default.
- Universal kriging– assumes that there is an overriding trend in the data, and it can be modeled by a deterministic function, a polynomial.
Perform kriging Interpolation in ArcMap
Interpolates a Raster surface from points using an Kriging technique.
Steps:
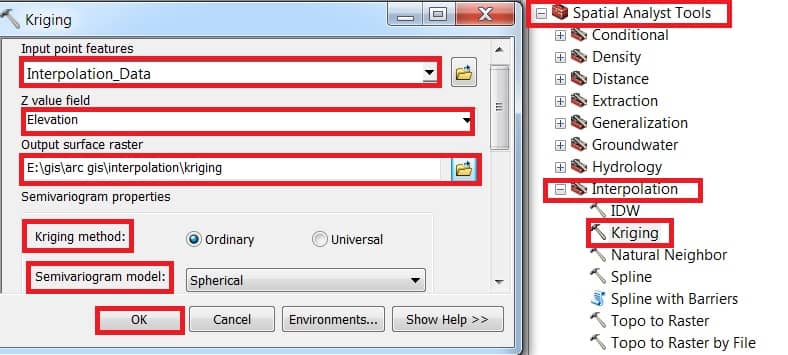
1.Open ArcToolbox, expand Spatial Analyst Tool > then expand Interpolation and select Kriging.
2. Kriging window appears, select Input point features data (Interpolation_Data), Z value field select Elevation, then choose Output raster destination. Select Kriging method – Ordinary and choose Semivariogram model. Finally, click the OK button.
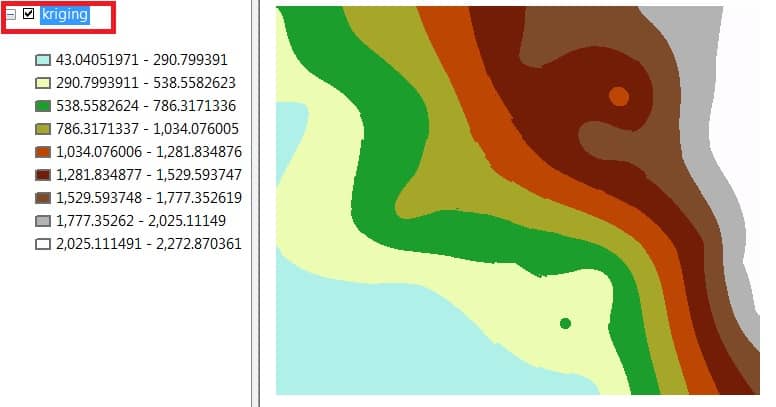
Now show to your Kriging result in ArcGIS Map View.
Perform Kriging in ArcGIS Pro
1. Enable Geostatistical Analyst Extension:
- Go to
Project→Licensing→ ensure Geostatistical Analyst is enabled.
2. Prepare Your Data:
- Input: Point feature layer with known values (e.g., rainfall, elevation).
- Make sure it has a projected coordinate system.
3. Open Kriging Tool:
- Go to
Analysis→Tools→ search for Kriging or Empirical Bayesian Kriging.
4. Set Parameters:
- Input point features: Your data layer.
- Z value field: Attribute to interpolate.
- Choose kriging type, search radius, and semivariogram model.
5. Preview & Validate:
- Use the Geostatistical Wizard for interactive model fitting, variogram modeling, and cross-validation.
6. Generate Output:
- A geostatistical layer is created (can be exported to raster using GA Layer to Grid).