Surface Analysis in GIS
Surface Analysis represents height values for an Elevation surface or structure of a Surface. In this Tutorial, learn How to create different types of Surface Analysis map in ArcGIS.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Slope | Measures the steepness or degree of incline of a surface. |
| Aspect | Direction a slope faces (e.g., north, south). |
| Hillshade | Simulates how terrain is illuminated based on sun angle. |
| Viewshed | Area visible from a specific point. Useful for placing towers, lookout points. |
| Contour Lines | Lines connecting points of equal elevation. |
| Watershed | Region draining into a river or lake. |
Now perform 6 Surface Analysis model.
Launch ArcGIS Software, then open the Toolbox, ArcToolbox window is appears to expend Spatial Analyst Tools, then expend the Surface subgroup. All are surface analysis models available in this group. Select and double click it.
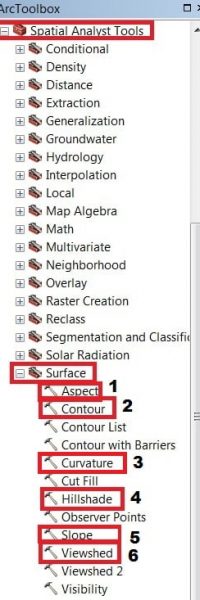
Create Surface Analysis Map in ArcGIS
In ArcMap, creating surfaces using Spatial Analyst Tools (slope raster from elevation).
1. Aspect
The Aspect identifies the down-slope direction of the maximum rate of change in value from each cell to its neighbors. Now Aspect can be thought of as the slope direction.
Open Aspect. The Aspect window appears to select Input Raster, and Output Raster, and click OK.
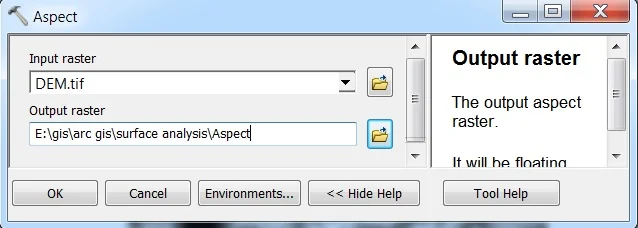
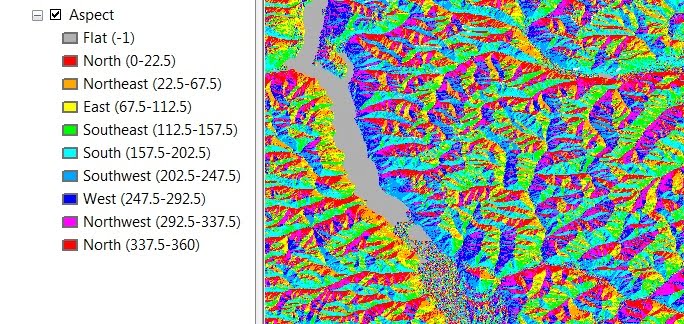
2. Contour
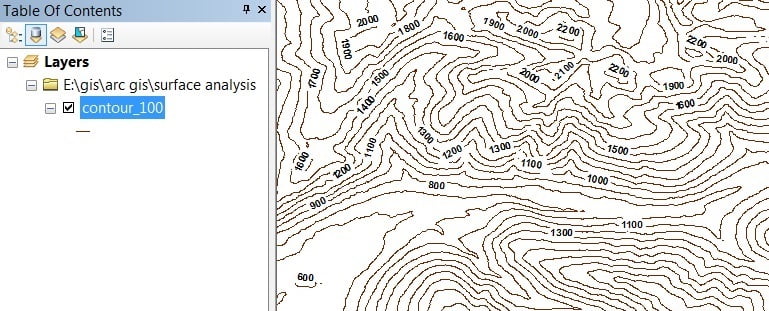
Contours are line features that connect locations of equal elevation value in a raster dataset. That represents continuous phenomena such as elevation.
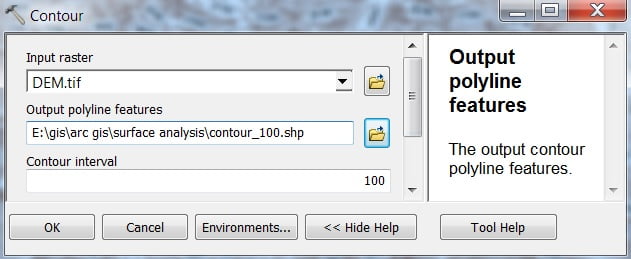
Open Contour. The Contour window appears to select Input Raster, Output Features, and the most important input contour interval (ex.- 100), then click OK.
3. Curvature
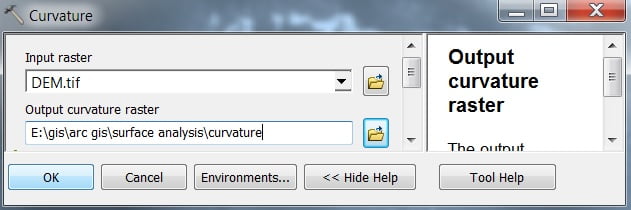
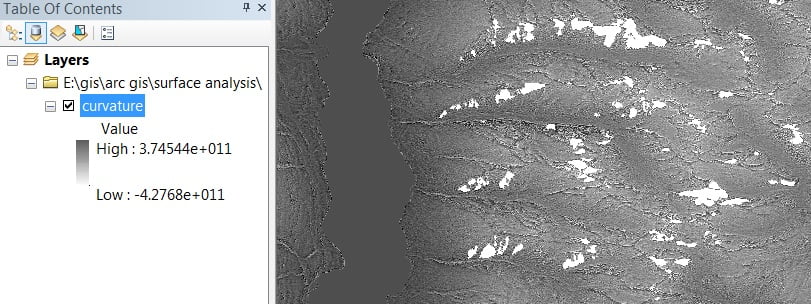
Curvature represents, determine the acceleration and convergence of flow in a drainage basin to better understand topsoil erosion.
Open Curvature. The Curvature window appears to select Input Raster, and Output Raster, and click OK.
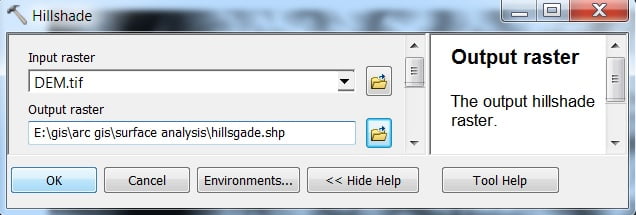
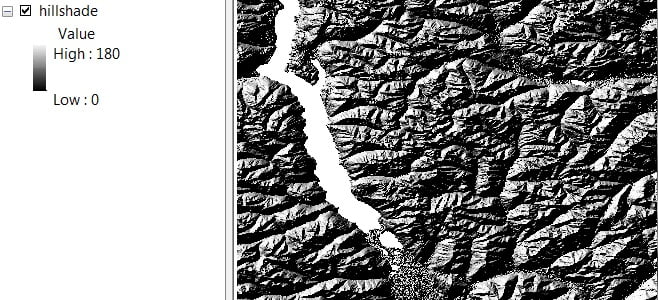
4. Hillshade
Create a Hillshade relief from an elevation surface raster by considering appropriate illumination source between Angel and Shadow.
Open Hillshade, The Hillshade window appears to select Input Raster, and Output Raster, and click OK.
5. Slope
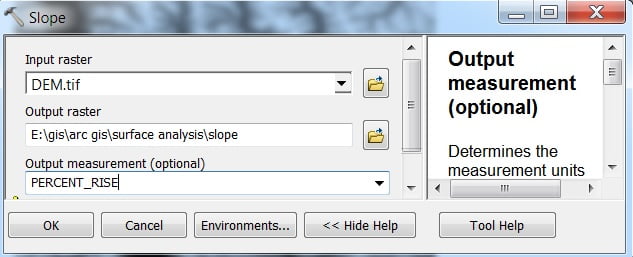
The Slope represents the variations of the landscape. You want to find the areas most at risk of landslide based on the angle of steepness in an area.
Open Slope, The Slope window appears to select Input Raster, and Output Raster (you can choose output measurement- Degree or Percent), and click OK.

6. Viewshed
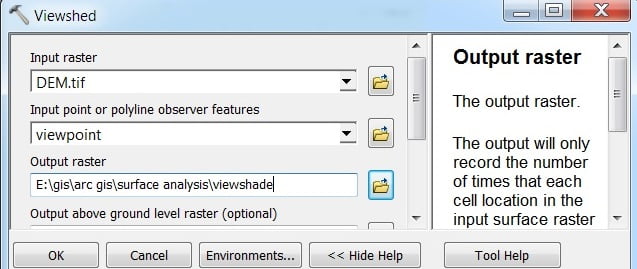
A Viewshed is useful when you want to know how visible objects will be. For instance, you might want to find the location with the most expansive view in an area. Because you want to choose the best location for an observation tower or scenic overlook.
Perform Viewshade first, create a Point Vector file and point out any particular place in your Raster data. Open Viewshade. The Viewshade window appears to select Input Raster, Input point feature, and Output Raster, and click OK.





Thank you for any other great article. Where else could anyone get that type of info in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I’m on the look for such information.