Mobile GIS
Introduction
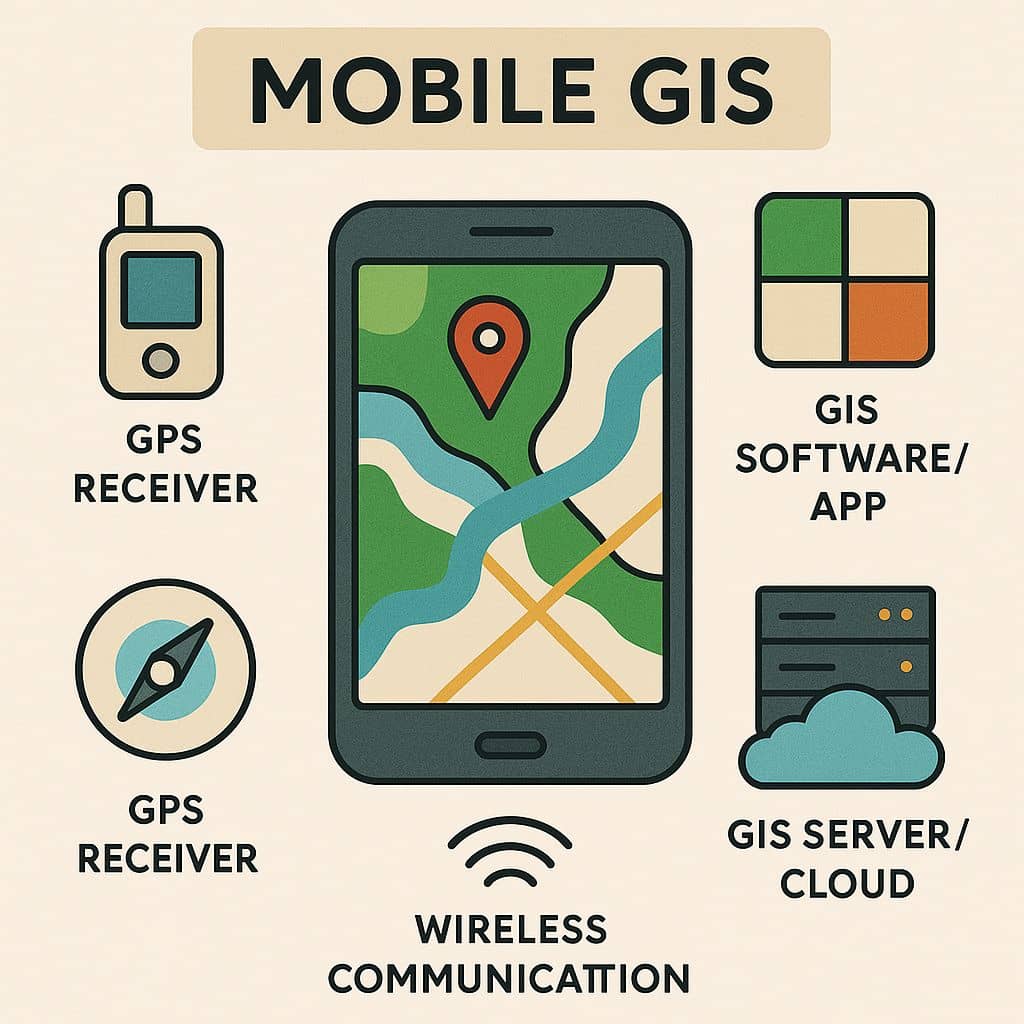
Mobile GIS is the expansion of GIS technology from enables field-based personnel to capture, store, update, manipulate, analyze, and display Geographic Information.
This is integrates one or more of the following technologies-
- Mobile devices
- Global positioning system (GPS)
- Wireless communications for Internet GIS access
Applications
- Field Mapping—Create, edit, and use GIS maps in the field.
- Asset Inventories—Create and maintain an inventory of asset locations and attribute information.
- Asset Maintenance—Update asset location and condition and schedule maintenance.
- Inspections—Maintain digital records and locations of field assets for legal code
- compliance and ticketing
- GIS Analysis and Decision Making—Perform measuring, buffering, geoprocessing, and
- Other GIS analysis while in the field.
Components
- Mobile GIS relies on the wireless network to transport information.
- Mob-GIS requires Internet enabled mobile devices. This means that the mobile devices
have to be able to access and display Internet services.
- Position determining components refer to components to determine the locations of the mobile devices in real time. They include hardware and software to identify and track the locations of mobile devices.
- Mob-GIS relies on the wireless network to transport information.
- Information processing service components concern the network processing or analysis
- services of geographic information.
Advantages
- Real-time data collection and updates
- Reduced paperwork and manual entry
- Increased fieldworker productivity
- Improved decision-making accuracy
Mobile Mapping
Mobile Mapping is the combination of geographic information system (GIS) software, global
positioning systems (GPS), and mobile computing devices. Mobile Mapping allows you to visualize information in a digital map, collect information where you observe it, and interact directly with the world around you, while improving productivity and data accuracy. Different terminology is used as mobile mapping or mobile GIS or mobile GPS, conveying the same
meaning.
Mobile mapping services are server based where the server delivers data and or processing to clients on demand. Geographic services receive requests for geographic data and processing, e.g., make a map, geo-code an address, download data for an area.
5 Field Mobile GIS Apps for Data Collection
Architecture of Mobile GIS
The architecture of mobile GIS is very similar to that of Internet-based GIS, using client-server architecture. Client-server applications usually implement what is referred as three Tiered Architecture.
This architecture divides the application into a presentation tier, a business logic tier and a data management tier. Each tier can be replaced or updated without affecting the others.
The presentation tier consists of client side components, which are used to send requests to the server and to view the results (maps and data).
The business tier is the core of any solution and consists of the server side components including the Web server and application server.
The data management tier is responsible for the management of both spatial and attribute data in the application. In some cases, one server is used for both the business and data management tier. In other cases each tier can be on a separate server.
The architecture of Mob-GIS is very similar to the wire line-based internet GIS. It has three major components: the client, the server, and the network services. The traditional client in the Internet is a personal computer.