ISODATA
ISODATA is an iterative Self-Organizing Data Analysis Technique.
What is ISODATA?
The ISODATA algorithm stands for Iterative Self-Organizing Data Analysis Technique. It is an unsupervised classification method used primarily in remote sensing and image processing for clustering multispectral image data.
It uses spectral distance between image pixels in feature space to classify pixels into a specified number of unique spectral groups.
How Its Works
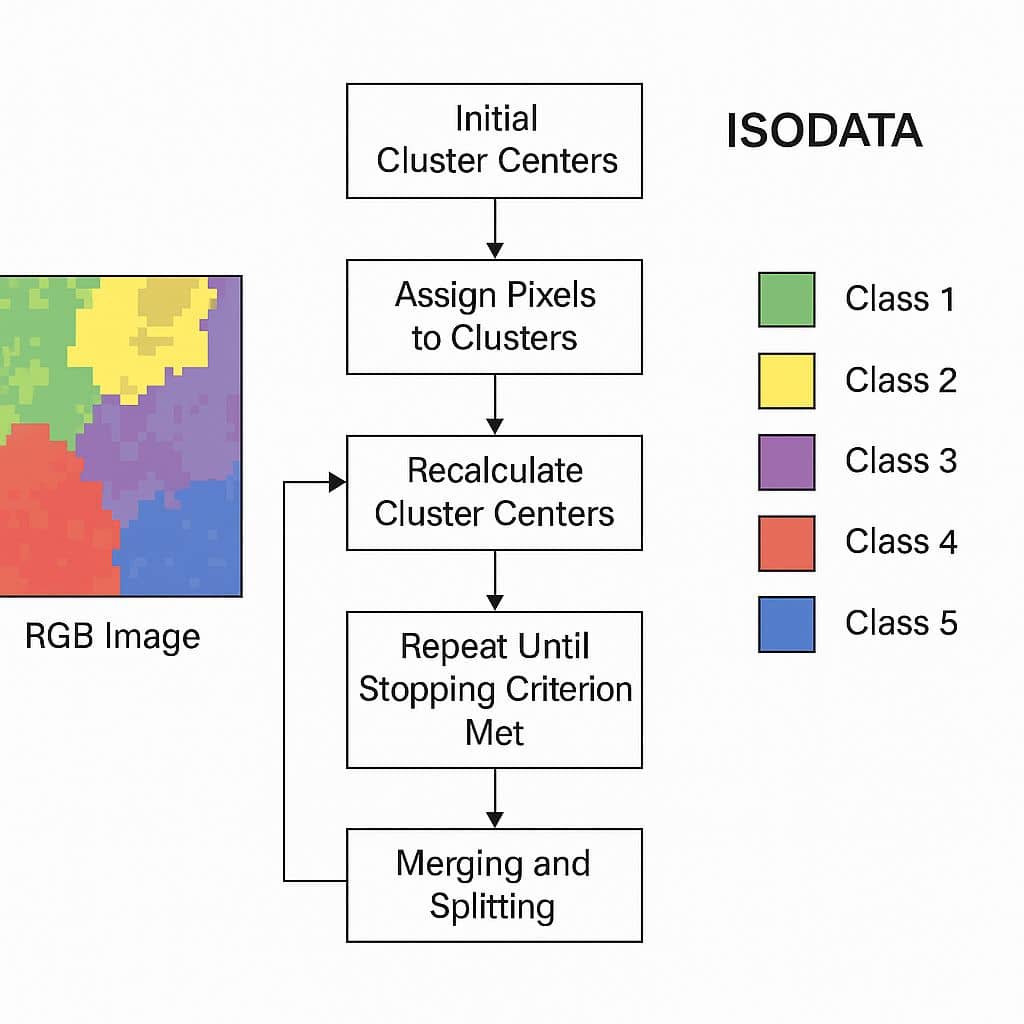
- Choose an initial number of clusters (e.g., 5).
- Assign each pixel to the closest cluster center (based on spectral distance).
- Recalculate cluster centers.
- Eliminate small clusters and merge/split as needed.
- Repeat until convergence.
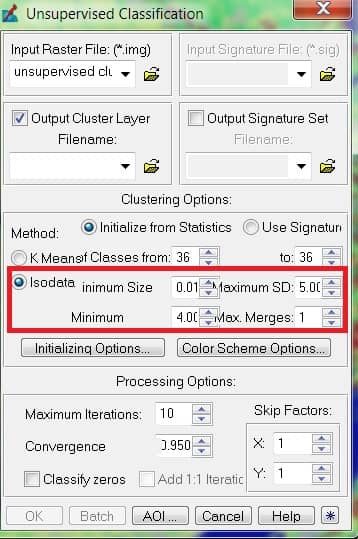
ISODATA Method in Unsupervised Classification
The ISODATA method uses minimum spectral distance to assign a cluster for each candidate pixel. The process begins with a specified number of arbitrary cluster means or the means of existing signatures, and then it processes repetitively, so that those means shift to the means of the clusters in the data.
ISODATA Clustering
To perform ISODATA clustering; NTM.
- N-maximum number of clusters to be considered. Since each cluster is the basis for a class, this number becomes the maximum number of classes to be formed. The process begins by determining N arbitrary cluster means. Some clusters with too few pixels can be eliminated, leaving less than N clusters.
- T-a convergence threshold, which is the maximum percentage of pixels whose class values are allowed to be unchanged between iterations.
- M-maximum number of iterations to be performed
Clustering Parameters
- Number of clusters: 10 to 15 per desired land cover class.
- Convergence threshold: percentage of pixels whose class values should not change between iterations; generally set to 95%.
- Maximum number of iterations: ideally, the convergence threshold should be reached. Should set “reasonable” parameters so that convergence is reached before iterations run out.
ISODATA Iteration
An ISODATA iterations, pixels assigned to clusters with the closest spectral mean; mean recalculated; pixels reassigned.
Continues until maximum iterations or convergence threshold reached.
Applications of ISODATA in Remote Sensing
- Land use/land cover classification
- Vegetation and crop analysis
- Mineral and soil mapping
- Environmental change detection




