Panchromatic Sensor in Remote Sensing
The Panchromatic (PAN) Sensor had 5.8 m spatial resolution, as well as stereo capability. Its swath width is 70 m. Revisit time was every five days, with ± 26° off-nadir viewing.
Panchromatic Band
| Band | Wavelenth (µm) |
|---|---|
| pan | 0.5 to 0.75 |
Key Features of Panchromatic Image
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Single band (black-and-white) |
| Wavelength Range | ~0.5 µm to 0.75 µm (Visible spectrum) |
| Resolution | Typically high spatial resolution |
| Appearance | Grayscale image (brighter areas reflect more light) |
| Use | Often used for detailed analysis or as a base for pan-sharpening multispectral images |
Panchromatic Imagine
A panchromatic imagery uses a single band image. This imagery is extremely useful, as it is a much higher spatial resolution than the multispectral imagery from the same satellite. For example, the QuickBird satellite produces pan imagery having a pixel equivalent to an area 0.6 m × 0.6 m (2 ft × 2 ft), while the multi-spectral pixels represent an area of 2.4 m × 2.4 m (8 ft × 8 ft).
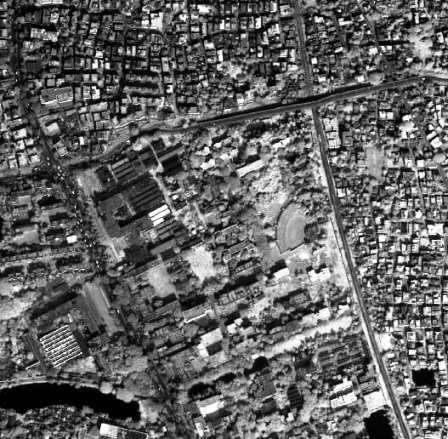

Color Composites With Panchromatic Band
The process of sharpening color composites with the pan band can be performed using 3 most common of them:
- HSV (Higher Spatial Resolution) Sharpening
- Gram-Schmidt Pan-Sharpening
- The Brovey Transformation
Applications
- Urban area mapping
- Edge detection and feature extraction
- High-resolution base maps
- Pan-sharpening: improving the spatial resolution of multispectral images