Understanding ArcPy: Python for ArcGIS Automation
Introduction to ArcPy
From Clicks to Code: Unlocking the Secret Powers of ArcPy
If you’ve ever wanted your GIS processes to be quicker, more intelligent, and less reliant on clicks, you’re in good company. ArcPy, the robust Python library designed for ArcGIS, converts tedious geoprocessing tasks into neat, reusable code —helping you save time and enhance productivity. However, ArcPy offers more than just an easy way to create buffers and clips.

This guide will lead you from basic automation to sophisticated techniques, even demonstrating how to create your own mini-GIS tools with a user-friendly graphical interface.
Step-by-Step Guide to ArcPy for Beginners
Step 1: Begin with Simplicity – Automate a Basic Buffer
Buffering is a fundamental task in GIS. Picture having a layer of schools and needing to generate a 700-meter buffer surrounding each one.
Using ArcPy, it only takes a handful of lines:
Why it’s important: This streamlines a cumbersome multi-click manual process, allowing you to repurpose code for various datasets or effortlessly scale to hundreds of features.
________________________________________
Step 2: Modify Fields Using Python Logic
ArcGIS’s Field Calculator has its constraints. ArcPy enables you to implement comprehensive Python logic to modify attribute fields.
Example: Adjust student capacity according to the type of school.
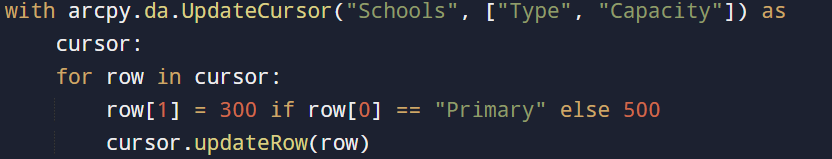
Advantages:
- Can be reused for any field update logic.
- Accommodates intricate custom rules.
- Optimized for handling large datasets.
Step 3: Efficiently Batch Process Datasets
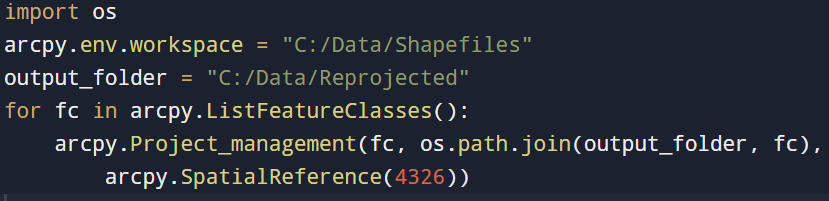
Looking to reproject 50 shapefiles to WGS 1984? Creating a loop simplifies this task:
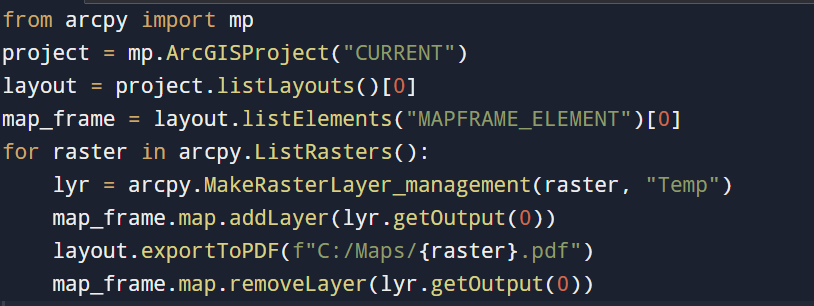
Need a separate map for each district or month? The arcpy.mp module in ArcGIS Pro allows ArcPy to automate layout exports:
When to apply:
- Large national initiatives
- Automated workflows
- Multi-client geoprocessing
Using ArcPy for batch processing turns laborious manual tasks into swift, automated scripts.
________________________________________
Step 4: Automatically Export Map Series
Automates layout exports:
Applications:
- Time-series mapping
- District-level analysis
- Automated map generation
This enhances efficiency when creating numerous similar maps. _______________________________________
Step 5: Convert Scripts into Custom ArcGIS Tools
Do you want to easily share your scripts with your team? Transform them into script tools:
- Generate a toolbox (.tbx)
- Incorporate your Python script
- Set up inputs/outputs as GUI components, why?
- Facilitate workflow sharing within teams
- Implement error handling and validation
- Standardize and reuse workflows
Custom tools render your automation user-friendly for those less versed in coding. ________________________________________
Step 6: Integrate Live APIs for Real-Time GIS
ArcPy can retrieve live data from APIs to dynamically enhance your GIS layers.
For instance: Access the current temperature from a weather API and refresh a city layer:
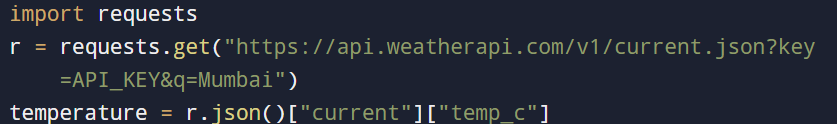
Integrate this with ArcPy cursors to ensure your spatial data mirrors real-world changes almost instantly.
________________________________________
Step 7: Intelligent Rule-Based Spatial Analysis
ArcPy empowers spatial modeling based on logic. For example, identify the most suitable sites for solar energy installations by combining raster criteria:
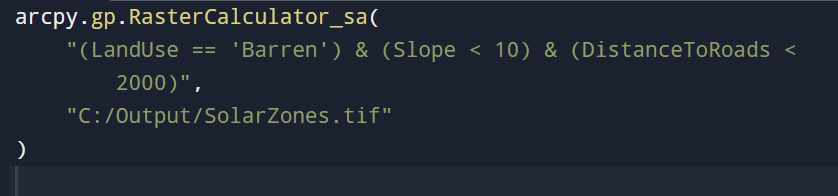
Ideal for:
- Urban development
- Assessing environmental hazards
- Optimizing infrastructure
This enables sophisticated geospatial decision-making.
________________________________________
BONUS: Design a GUI using Tkinter (Indeed, You Can!)
Looking to build your own compact GIS application? Tkinter, Python’s native GUI library, allows you to create simple user interfaces that initiate ArcPy functions — eliminating the need to manually launch ArcGIS.
Why opt for Tkinter?
- Quickly design input forms, buttons, and windows
- Enhance user accessibility for non-developers
- Streamline repetitive processes with a single click
Let’s create a mini buffer tool interface.
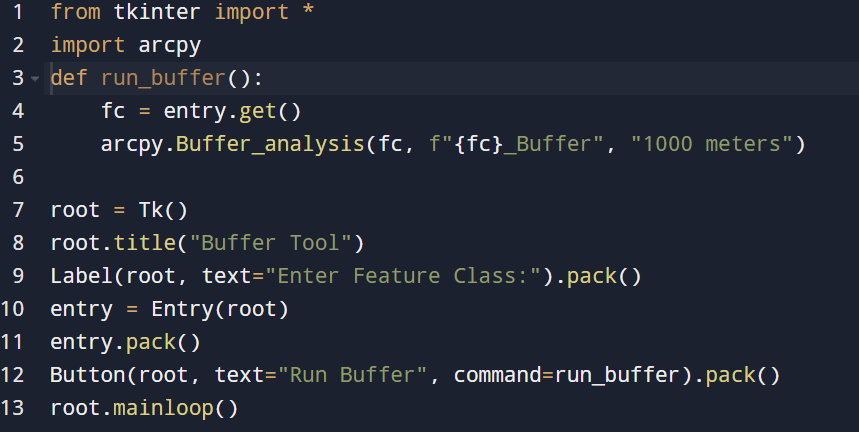
Users enter a layer name, click the “Run Buffer” button, and watch as ArcPy seamlessly operates in the background.
________________________________________
Conclusion: What you’ve just learned
ArcPy goes beyond being merely a scripting library — it acts as a productivity tool for GIS professionals.
With this tool, you can:
- Automate essential geoprocessing functions like creating buffers and updating fields
- Process multiple datasets and layers simultaneously with ease
- Effortlessly export high-quality maps
- Design tailored toolboxes equipped with user-friendly interfaces
- Pull live data from APIs to improve your spatial analysis
- Build rule-based spatial models for complex decision-making tasks
- Develop desktop applications that enhance GIS operations




