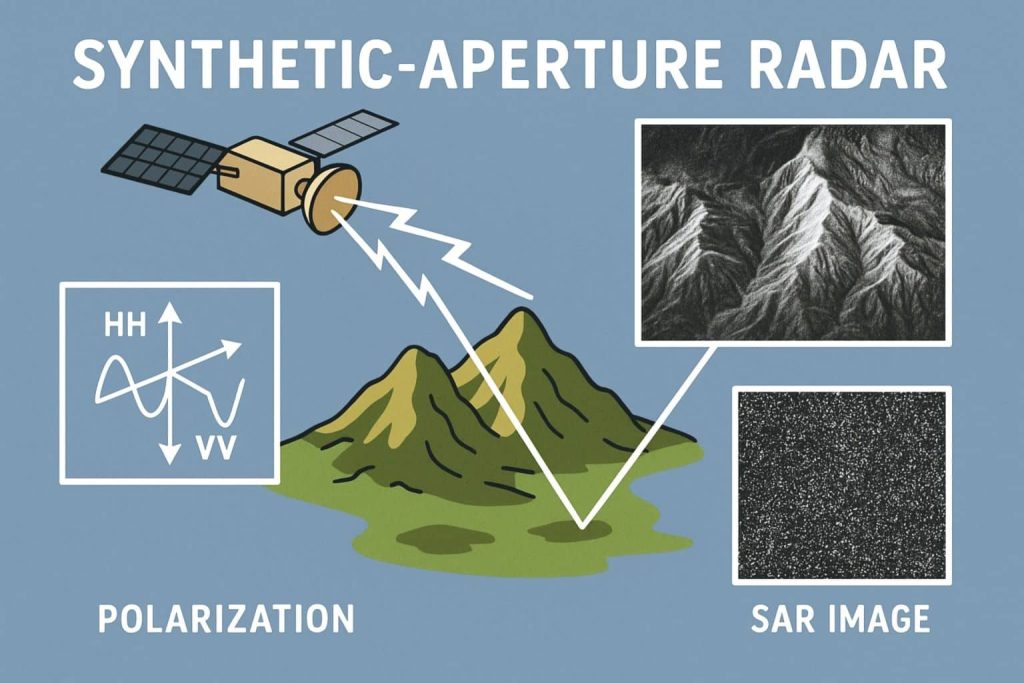
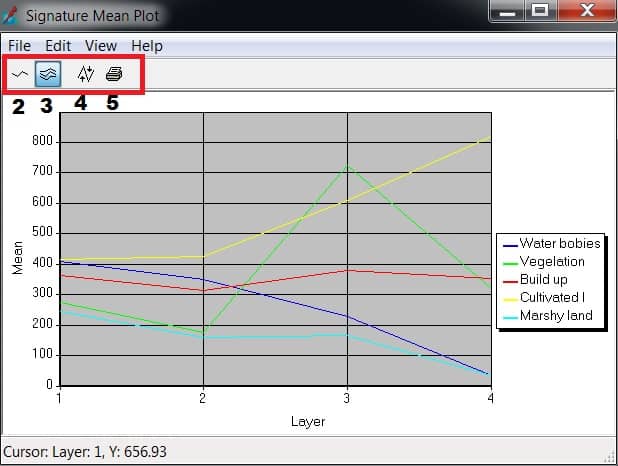
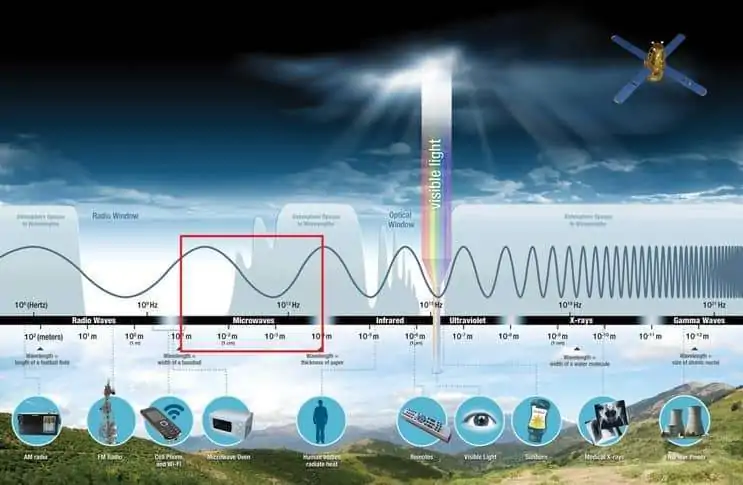
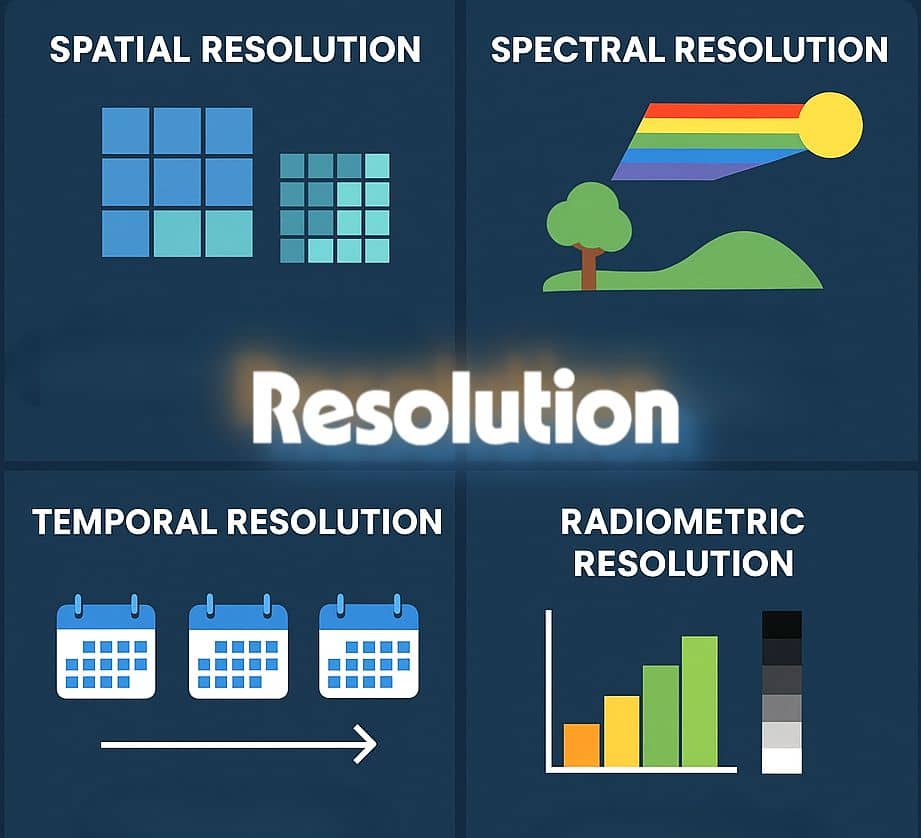
Synthetic Aperture Radar
Summary: – Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an active remote sensing technology that uses microwave radar signals to create high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, regardless of weather conditions or daylight. What is Synthetic Aperture Radar? A Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an airborne or spaceborne side looking Radar system which utilizes the flight path […]