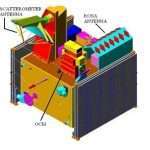
Remote Sensing Satellite
Remote Sensing (RS) technology based on Satellites system. This technology began with the early use of Aerial Photography, then it’s shifted satellites. These satellites orbit the Earth and capture images or data in various wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as visible, infrared, or microwave.
Remote sensing satellites are also called Earth observation satellites. They’re used for environmental monitoring (atmosphere, ocean, and land), meteorology, and cartography.
The first occurrence of remote sensing satellites on October 4, 1957, with the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1. NASA launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, on January 31, 1958.
How Remote Sensing Satellite work?
The Remote sensing by satellite will capture electromagnetic radiation on the microwave, ultraviolet, infrared, and visible wavelengths radiated, scattered, or reflected from the Earth.
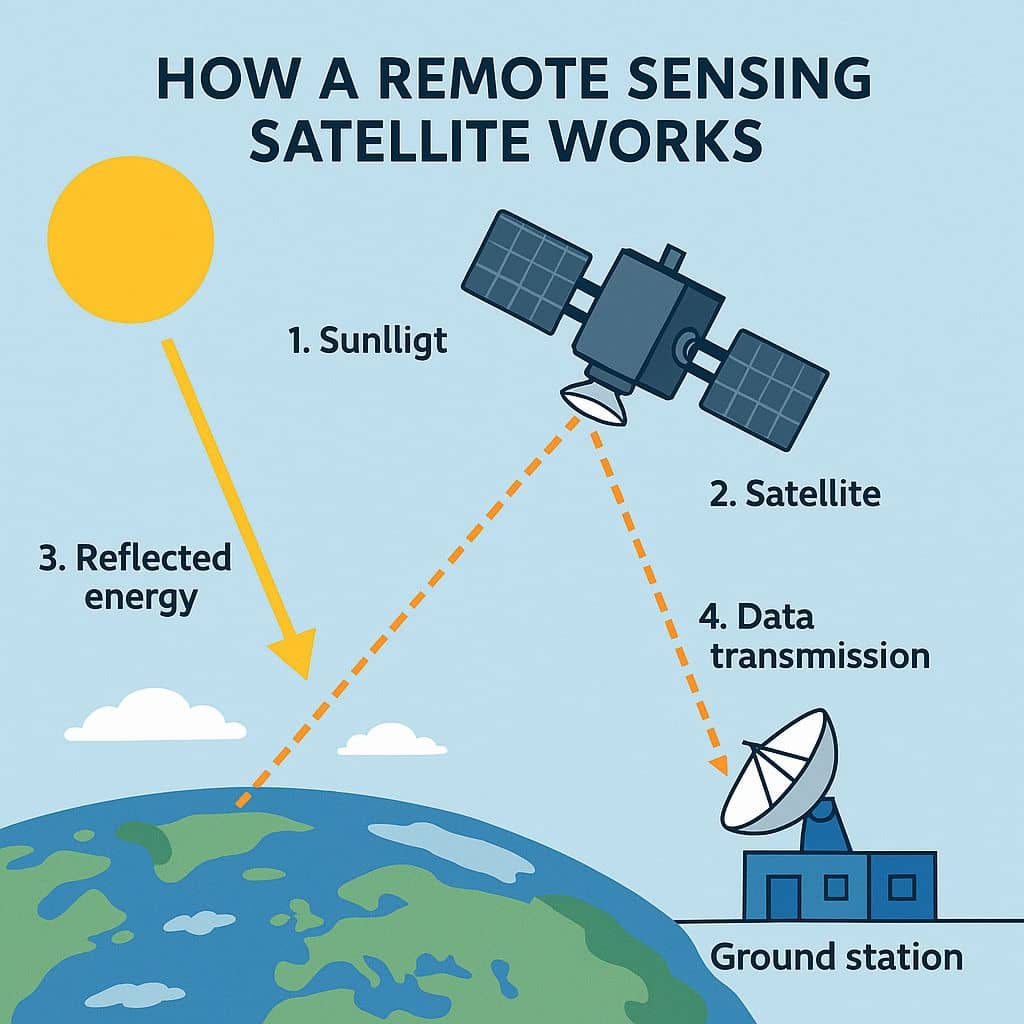
1. Energy Source
- Most commonly the Sun (for passive sensors).
- Some satellites use their own energy source (e.g., radar signals in active sensors).
2. Interaction with Earth
- Sunlight hits the Earth’s surface.
- The surface reflects or emits energy depending on its properties (like vegetation, water, soil, etc.).
3. Detection by Satellite Sensor
- The satellite sensor detects the reflected or emitted energy.
- Types of data collected: visible light, infrared, microwave, thermal, etc.
4. Data Transmission
- The satellite sends the collected data to a ground receiving station.
5. Data Processing
- The data is converted into images or datasets.
- Analysts interpret this data for various applications (e.g., land cover mapping, agriculture monitoring, disaster response).
Types of Remote Sensing Satellites
1. Passive Remote Sensing Satellite
- Detect natural energy (mostly sunlight) reflected or emitted by objects.
- Example: Landsat series, Sentinel-2, MODIS.
2. Active Remote Sensing Satellite
- Emit their own signals (like radar or laser) and measure the reflection.
- Example: RADARSAT, Sentinel-1 (SAR), TerraSAR-X.
There are two types of sensors working in RS System:
Common Remote Sensing Satellites
Characteristics of representative satellites
| Satellites | Spatial resolution (meters) | Revisit time (days) | Spectral range (μm) number of bands | Number of bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat | 15–120 | 16 | 0.45–12.5 | 11 |
| ASTER | 15–90 | 15 | 0.52–11.65 | 15 |
| SPOT | 10–20 | 26 | 0.45–1.75 | 5 |
| IKONOS | 1–4 | 1–4 | 0.45–0.90 | 5 |
| Quickbird | 0.61–0.72 | 1–6 | 0.45–0.9 | 4 |
| IRS | 5.8–70 | 5–24 | 0.52–1.7 | 4 |
| WorldView-2 | 0.46–2.4 | 1.1–3.7 | 0.4–1.05 | 8 |
| WorldView-3 | 0.31–30 | <1.0–4.5 | 0.40–23.6 | 26 |
| WorldView-4 | 0.31–1.24 | <1.0–4.5 | 0.65–0.92 | 4 |
| Sentinel-2 | 10–60 | 5 | 0.04–2.19 | 12 |
| GeoEye | 0.46–1.84 | 2.1–8.3 | 0.45–0.92 | 4 |
Primary Applications of representative satellites:
| Satellites/Sensor | Applications |
|---|---|
| Landsat | Global-change research, agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance, education |
| ASTER | Vegetation and ecosystem dynamics, land surface temperature, geology, hazard monitoring, land-cover change, land surface climatology, hydrology |
| SPOT | Exploring the Earth’s resources, detecting and forecasting phenomena involving climatology and oceanography, and monitoring human activities and natural phenomena |
| IKONOS | Urban geography, land-use, agriculture, and natural-disaster management |
| Quickbird | Map publishing, land and asset management, and risk assessment |
| IRS | Applications in forestry, agriculture, environment, soil characteristics, wasteland identification, flood and drought monitoring, ocean resource development, mineral exploration, land use and monitoring of underground and surface water resources. |
| WorldView | Mapping clouds, ice, snow and correcting for aerosol and water vapor |
| Sentinel-2 | Land and maritime monitoring, emergency management, and surveillance |