Aerial Photography
What is Aerial Photography?
Aerial photography is the process of taking photographs of the Earth’s surface from an elevated position, typically using aircraft, helicopters, balloons, blimps, dirigibles, rockets, parachutes. In recent times, using ‘Drone’ to capture Aerial Photographs.
It plays a critical role in Remote Sensing, mapping, GIS, environmental monitoring, and urban planning.

In Photographs the locations of which determined by ground-surveying techniques this technique known as photogrammetry. However, it involves each simultaneous projection of overlapping views. Makes possible the preparation of contour maps or three-dimensional models of the terrestrial surface that has been photographed. Valuable data on Topography, Geology, Hydrology, Soil and Vegetation, Ocean currents, and resources have become accessible with this use of satellite technology and expert interpretation.
Types of Aerial Photography
1. Based on Camera Orientation:
- Vertical (Nadir): Taken with the camera pointing straight down; useful for mapping.
- Oblique:
- Low Oblique: Slight tilt; horizon not visible.
- High Oblique: Larger tilt; horizon visible.
2. Based on Spectrum:
- Panchromatic (black and white)
- Color (visible spectrum)
- Color Infrared (CIR): Useful in vegetation and water body analysis.
- Thermal Infrared: Measures heat emission.
- Multispectral / Hyperspectral
3. Based on Platform:
- Fixed-Wing Aircraft
- Helicopters
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)/Drones
- Satellites
Download Aerial Imagery
Earth Explorer
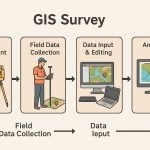
Downloading Aerial Imagery using USGS Earth Explorer.
1. Navigate Earth Explorer, it is composed of the Search Criteria and the Map Viewer components.
2. Select Data Sets, expand Aerial Imagery, and choose your data.
3. Now Download Data.
Open Aerial Map
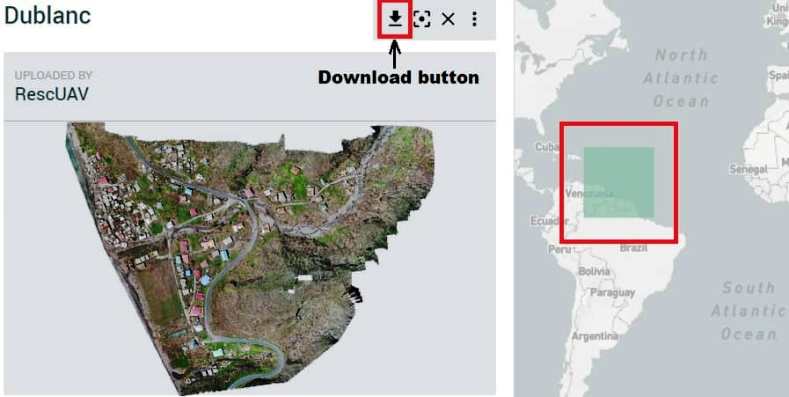
OpenAerialMap (OAM) is a set of tools for searching, sharing, and using openly licensed aerial imagery.
1. Open OAM online portal.
2. Click any ware on the map screen, and show the result on the left side.
3. Select your data, and click the download button.
Key Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Photogrammetry | Science of making measurements from aerial photos |
| Stereoscopy | Viewing 3D scenes from overlapping photo pairs |
| Orthophoto | Geometrically corrected aerial photo |
| Flight Plan | Pre-planned path for systematic aerial photo coverage |
| Scale | Ratio of photo distance to ground distance |
Concept of Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the Art, Science, and Technology of obtaining probable information about physical objects and the Environment. Through the process of recording, measuring, and interpreting photographic images and patterns of Electomangetic Radiant energy and other phenomena.
Digital photogrammetry is photogrammetry as applied to digital images that are stored and processed on a computer. Digital images can be scanned from photographs or can be directly captured by digital cameras. Many photogrammetric tasks can be automated in digital photogrammetry. Digital. The output products are in digital form, such as digital maps, DEMs, and digital ortho photos saved on computer storage media. With the development of digital photogrammetry, photogrammetric techniques are more closely integrated into Remote Sensing and GIS.
Process of Photogrammetry
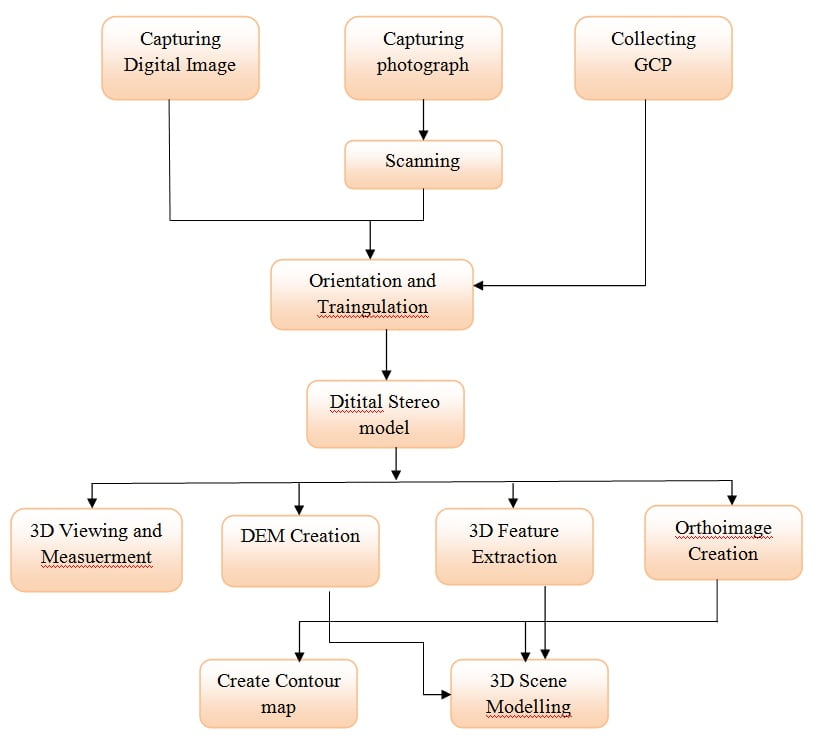
Geometry of Aerial Photography
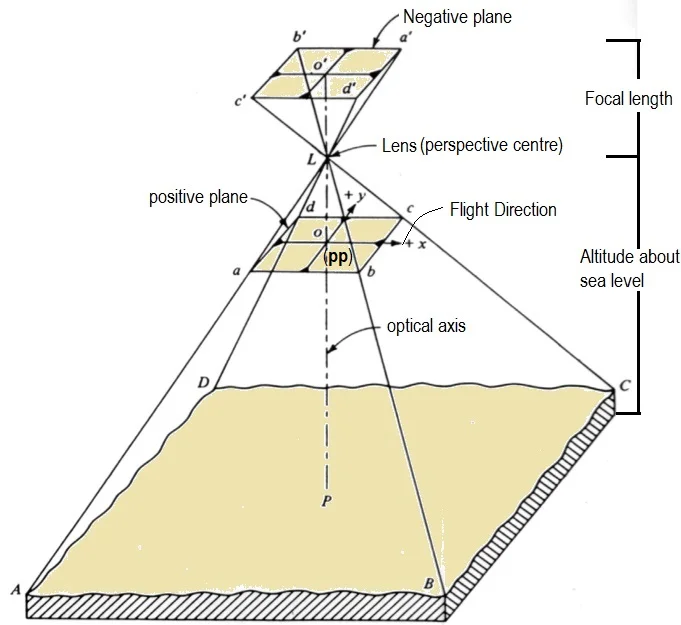
A photographic image is a central perspective. Here implies that every light ray, which reaches the film surface during exposure, passed through the camera lens. Photography implies the position of all the points is controlled by a single point of the image, which controls the Geometry of the entire photographs.
Principal point (PP)- in the point on the image where the optical axis intersects the image plane. The Optical axis is an imaginary line that passes through the optical center of the lens and perpendicular to the film or image plane.
The Distance between the perspective center and principal point determines the Focal length.
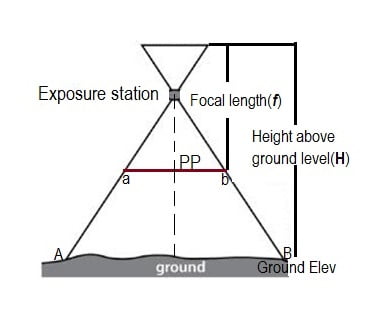
Seale of Photography
The Scale (S) of the Aerial photograph can be computed either by considering the ratio of the flying height (H) above the ground and the focal length (f) or by the ratio of a known distance in the photograph (ab) and the distance on the ground (AB).
Formula :
Scale (S) = f/H or ab/AB
Applications
- Topographic Mapping
- Land Use / Land Cover Analysis
- Agriculture Monitoring
- Disaster Management
- Urban and Regional Planning
- Archaeological Surveys
- Military Reconnaissance
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aerial Photography
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Large area coverage in a single shot ✅ High spatial resolution (especially from drones or low-altitude flights) ✅ Useful historical record when time series of images are available ✅ Can be used where satellite data is limited due to cloud cover | ❎ Weather dependent (especially for optical imagery) ❎ Costlier than satellite imagery for repeated coverage ❎ Requires georeferencing and orthorectification for mapping accuracy |