ArcGIS Field Data Types
ArcGIS Data Types
In ArcGIS, data types are critical for managing spatial and attribute information. ArcGIS supports a variety of data types broadly categorized into spatial (geographic) and non-spatial (attribute or tabular) data.
File Geodatabase are the same as data types.
ArcGIS Field Data Types
When you create or manage an attribute table (such as in a shapefile or geodatabase feature class), each field (column) must have a field data type that defines the kind of data it stores.
In ArcGIS Desktop 4 Numeric data type:
- Short integer
- Long integer
- Float (single-precision floating-point numbers)
- Double (double-precision floating-point numbers)
ArcGIS Geodatabase Data Description
The following table lists for file and personal Geodatabase’s data types, their ranges, and storage requirements.
| Data type | Storable range | Size (Bytes) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short integer | -32,768 to 32,767 | 2 | Numeric values without fractional values within specific range; coded values |
| Long integer | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | 4 | Numeric values without fractional values within specific range |
| Float (single-precision floating-point number) | approximately -3.4E38 to 1.2E38 | 4 | Numeric values with fractional values within specific range |
| Double (double-precision floating-point number) | approximately -2.2E308 to 1.8E308 | 8 | Numeric values with fractional values within specific range |
Data type, Precision, and Scale
Data types and their possible precision and scale values you can set in ArcGIS Desktop.
| Data type | Precision (maximum field length) | Scale (maximum number of decimal places) |
|---|---|---|
| Short integer* | 1–5 (Oracle) | 0 |
| Long integer** | 6–9 (Db2 and Informix)6–10 (Oracle) | 0 |
| Float | 1–6 | 1–6 |
| Double | 7+ | 0+ |
Number ranges and store them in a database or desktop Geodatabase
| Range | Data type | Precision (field length) | Scale (decimal places) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 to 99 | Short integer | 2 | 0 |
| -99 to 99* | Short integer | 3 | 0 |
| 0 to 32,767* | Short integer | 5 | 0 |
| 32,768 to 99,999 | Long integer | 5 | 0 |
| 0.001 to 0.999 | Float | 4 | 3 |
| 1,000.00 to 9,999.99 | Float | 6 | 2 |
| -123,456.78 to 0* | Double | 9 | 2 |
| 0 to 1,234.56789 | Double | 9 | 5 |
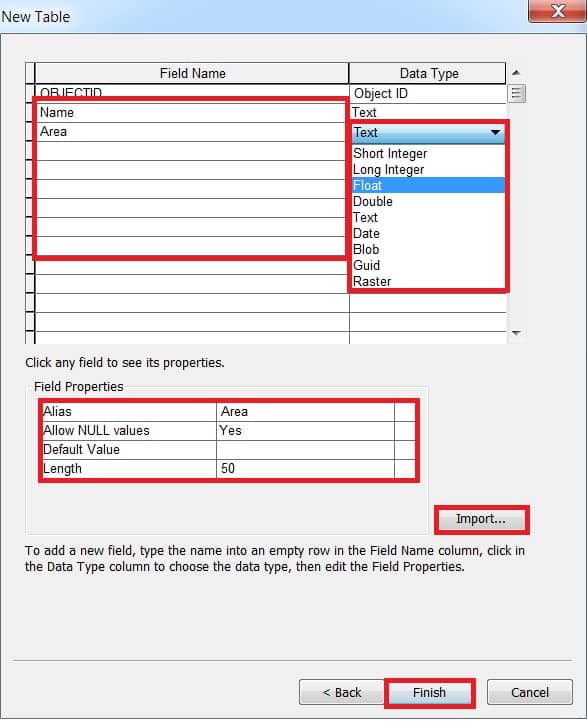
Field Data Types and Descriptions
You create a Feature class or table in ArcGIS, there are 11 different data types available for each column.
| Data type | Access data type |
|---|---|
| OBJECTID | Long Integer |
| SHORT INTEGER | Integer |
| LONG INTEGER | Long Integer |
| FLOAT | Single |
| DOUBLE | Double |
| TEXT | Text |
| DATE | Date/Time |
| BLOB | OLE Object* |
| GUID | Number |
| GEOMETRY | OLE Object* |
| RASTER | Long Integer |
| Field Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Short Integer | Stores small whole numbers | 1, 25, -32768 |
| Long Integer | Stores large whole numbers | 100000, -2147483648 |
| Float | Single-precision floating point numbers (decimal with ~6 digits of precision) | 123.45 |
| Double | Double-precision floating point numbers (decimal with ~15 digits of precision) | 1234567.8901234 |
| Text (String) | Stores alphanumeric characters. Length must be defined. | "River Name", "ID001" |
| Date | Stores date and time information | 2025-07-29 10:30:00 |
| Blob | Stores binary large objects (images, documents, etc.) | Used internally, not human-readable |
| GUID | Globally Unique Identifier (for relationships between tables) | A23C5B2F-8F3D-4A4E-8125-5B1B27F3E10B |
| Global ID | A special GUID field automatically managed by ArcGIS for unique identification | Same format as GUID |
| Raster | Stores raster datasets in a geodatabase | Internal raster storage |
| Geometry | Stores the shape (point, line, polygon) – not user-defined | Automatically created for spatial data |
DBMS Data Type in ArcGIS
In ArcGIS, when using Database Management Systems (DBMS) like SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, etc., the data types used in geodatabases are mapped between ArcGIS type and the underlying DBMS data type.
Here’s a breakdown of how ArcGIS field types map to DBMS-native data types:
ArcGIS Field Types vs. DBMS Data Types
| ArcGIS Field Type | SQL Server | Oracle | PostgreSQL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short Integer | smallint | NUMBER(5) | smallint |
| Long Integer | int | NUMBER(10) | integer |
| Float | real | FLOAT(24) | real |
| Double | float | FLOAT(53) | double precision |
| Text (String) | nvarchar(n) or varchar(n) | VARCHAR2(n) | varchar(n) |
| Date | datetime | DATE or TIMESTAMP | timestamp |
| Blob | varbinary(max) | BLOB | bytea |
| GUID | uniqueidentifier | RAW(16) | uuid |
| Raster | Managed by ArcGIS (not native field) | ||
| Geometry/Shape | geometry or geography | SDO_GEOMETRY | geometry (PostGIS) |


